Ever wondered how to level up your management game and become a true leader in the MARKENDIUM SMPS world? Get ready to dive deep into Domain 6 Management, the secret sauce for success in this fast-paced, dynamic field. Think of it like the ultimate cheat sheet for navigating the complexities of managing projects, people, and resources – all while keeping the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge as your guiding star.
This journey will equip you with the tools, techniques, and real-world insights to not only understand the fundamentals of Domain 6 Management but to master its intricacies. From the core principles to the key processes and activities, we’ll break down the essential elements that make up this critical domain.
We’ll also explore practical examples, analyze cutting-edge tools, and even delve into a book review to give you a real-world perspective on how Domain 6 Management is implemented in practice.
Domain 6 Management
Domain 6 Management within the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge is a critical component of effective SMPS design, installation, and maintenance. It encompasses a comprehensive understanding of the operational aspects of SMPS systems, ensuring their seamless integration into larger electrical systems and their long-term reliability.
This domain focuses on the management of SMPS systems from a practical perspective, considering the real-world challenges and complexities that arise during their implementation and operation.
Core Principles of Domain 6 Management
The core principles of Domain 6 Management are grounded in the fundamental concepts of SMPS operation, encompassing efficiency, safety, and reliability. These principles guide the development and implementation of strategies for managing SMPS systems throughout their lifecycle.
- Efficiency:Maximizing the efficiency of SMPS systems is paramount. This involves optimizing the conversion process, minimizing energy losses, and ensuring that the system operates at its peak performance. Efficiency translates directly to lower operating costs and a reduced environmental footprint.
Domain 6 Management MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge is all about keeping things running smoothly, and that includes understanding the nuances of how things look. Just like how a master artist can make a character come alive with realistic folds and creases in their clothes, we need to know how to manage our resources and processes in a way that makes sense.
If you want to level up your understanding of how clothes drape and fold, check out Morpho Clothing Folds and Creases Anatomy for Artists (Morpho Anatomy for Artists 8). It’s a super cool resource that can help you visualize how things work, and that knowledge can translate into better management practices.
So, if you’re ready to level up your management game, check out that link and start thinking about the finer details of how things flow.
- Safety:The safety of personnel and equipment is paramount. Domain 6 Management emphasizes the implementation of robust safety protocols and procedures, including proper grounding, overcurrent protection, and isolation techniques. These measures ensure the safe operation of SMPS systems, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards.
- Reliability:SMPS systems are designed to provide uninterrupted power, making reliability a critical factor. Domain 6 Management addresses the maintenance and monitoring of SMPS systems, ensuring their consistent operation and minimizing downtime. This includes preventative maintenance, fault detection, and redundancy strategies to ensure continuous power delivery.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Effective Domain 6 Management requires a collaborative approach involving various roles and responsibilities. These individuals contribute to the overall success of the SMPS system throughout its lifecycle.
- SMPS Designer:Responsible for the initial design and specification of the SMPS system, ensuring it meets the specific requirements of the application. This role requires a deep understanding of SMPS technology, power requirements, and safety standards.
- Installation Technician:Responsible for the physical installation of the SMPS system, ensuring proper connections, grounding, and safety protocols are followed. This role requires hands-on experience with electrical systems and a thorough understanding of installation procedures.
- Operations Manager:Responsible for the day-to-day operation and monitoring of the SMPS system, ensuring its smooth and efficient operation. This role requires a strong understanding of SMPS systems, including performance metrics, fault detection, and maintenance requirements.
- Maintenance Technician:Responsible for the routine maintenance and repair of the SMPS system, ensuring its long-term reliability. This role requires specialized knowledge of SMPS systems, including troubleshooting, component replacement, and preventative maintenance techniques.
Real-World Scenarios
Domain 6 Management practices are essential in a variety of real-world scenarios where reliable and efficient power delivery is critical.
So, you’re all about that Domain 6 Management MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge, huh? You want to level up your game and become a total boss in the world of project management? Well, check out this awesome resource, Download And Listen Here , to get the lowdown on all the latest trends and best practices.
Once you’ve got that knowledge under your belt, you’ll be dominating the Domain 6 Management MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge like a pro!
- Data Centers:SMPS systems are crucial for ensuring uninterrupted power supply to critical servers and networking equipment in data centers. Effective Domain 6 Management minimizes downtime, protects valuable data, and ensures the smooth operation of these essential facilities.
- Hospitals:Hospitals rely on SMPS systems to provide reliable power to life-saving medical equipment. Domain 6 Management ensures the uninterrupted operation of these systems, preventing potential disruptions to patient care and critical medical procedures.
- Manufacturing Facilities:SMPS systems power production lines and critical machinery in manufacturing facilities. Domain 6 Management ensures the continuous operation of these systems, minimizing production downtime and maximizing productivity.
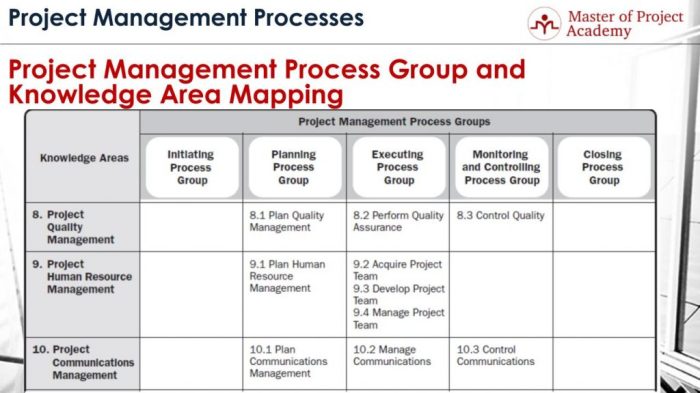
Key Processes and Activities
Domain 6 Management focuses on the critical processes and activities that ensure the efficient and effective operation of a MARKENDIUM SMPS system. These processes are interconnected, forming a robust framework that supports the overall success of the system.
Process Planning and Design
This process involves defining the overall structure and functionality of the MARKENDIUM SMPS system. It includes:
- Establishing clear objectives and goals for the system.
- Defining the scope of the system and its key components.
- Developing a detailed system architecture and design.
- Identifying and documenting the system’s functional and non-functional requirements.
This process sets the foundation for the entire MARKENDIUM SMPS system, ensuring that it aligns with business needs and objectives.
System Implementation
The system implementation process involves translating the design into a working system. This includes:
- Selecting and configuring the appropriate hardware and software components.
- Developing and deploying the necessary applications and interfaces.
- Integrating the system with existing systems and applications.
- Performing thorough testing and quality assurance activities.
This process ensures that the MARKENDIUM SMPS system is built according to the specifications and meets the defined requirements.
System Operations and Maintenance
This process focuses on the day-to-day operation and ongoing maintenance of the MARKENDIUM SMPS system. It includes:
- Monitoring system performance and identifying potential issues.
- Implementing proactive maintenance strategies to prevent system failures.
- Responding to system incidents and resolving issues promptly.
- Performing regular backups and disaster recovery planning.
- Ensuring system security and compliance with relevant regulations.
This process ensures that the MARKENDIUM SMPS system operates smoothly and reliably over its lifespan.
Performance Management
This process involves tracking and evaluating the performance of the MARKENDIUM SMPS system. It includes:
- Defining key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure system performance.
- Collecting and analyzing system data to track KPIs.
- Identifying areas for improvement and implementing corrective actions.
- Continuously optimizing system performance to meet evolving business needs.
This process helps to ensure that the MARKENDIUM SMPS system is operating efficiently and effectively.
Process Improvement
This process involves identifying and implementing improvements to the MARKENDIUM SMPS system. It includes:
- Conducting regular reviews of the system’s processes and procedures.
- Identifying opportunities for improvement and implementing changes.
- Utilizing process improvement methodologies such as Lean and Six Sigma.
- Continuously striving to enhance the system’s efficiency, effectiveness, and reliability.
This process ensures that the MARKENDIUM SMPS system remains relevant and adaptable to changing business needs and technological advancements.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
| Process | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) |
|---|---|
| Process Planning and Design |
|
| System Implementation |
|
| System Operations and Maintenance |
|
| Performance Management |
|
| Process Improvement |
|
Tools and Techniques for Effective Management
Domain 6 of the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge focuses on management. It’s not just about telling people what to do, but about guiding and empowering them to achieve their best. To do this effectively, you need the right tools and techniques.
This section explores some of the most valuable approaches to managing projects and teams.
Project Management Tools
Project management tools are essential for keeping track of tasks, deadlines, and resources. They help you stay organized, communicate effectively, and ultimately, deliver successful projects.
- Project Management Software:Tools like Asana, Trello, Jira, and Monday.com provide a central platform for task management, collaboration, and progress tracking. These platforms allow teams to create project plans, assign tasks, set deadlines, and monitor progress in real-time. The advantages include improved team communication, enhanced project visibility, and streamlined workflows.
However, implementing these tools can require initial setup and training, and there might be costs associated with using them.
- Kanban Boards:A visual method of project management that uses cards to represent tasks and moves them across different stages (To Do, In Progress, Done). Kanban boards provide a clear overview of project progress and highlight potential bottlenecks. The advantages include simplicity, flexibility, and visual representation of work.
However, Kanban boards might not be suitable for complex projects with intricate dependencies.
- Gantt Charts:A visual representation of project tasks, timelines, and dependencies. Gantt charts provide a clear roadmap for project execution, enabling managers to identify potential delays and adjust schedules accordingly. The advantages include a visual representation of project timelines and dependencies, facilitating effective planning and monitoring.
However, Gantt charts can be complex to create and maintain, especially for large projects.
Team Management Techniques
Effective team management involves fostering collaboration, motivating team members, and resolving conflicts. Several techniques can be employed to achieve these goals.
- Agile Methodologies:Agile methodologies like Scrum and Kanban emphasize iterative development, continuous feedback, and collaboration. They encourage teams to work in short sprints, adapt to changing requirements, and deliver value incrementally. The advantages include increased flexibility, improved collaboration, and faster delivery cycles.
However, agile methodologies require a shift in mindset and might not be suitable for all types of projects.
- Leadership Styles:Different leadership styles can impact team dynamics and performance. Transformational leadership inspires and motivates team members, while transactional leadership focuses on clear goals and rewards. The choice of leadership style should align with the team’s needs and project goals. The advantages include improved team morale, enhanced productivity, and increased employee engagement.
Domain 6 Management MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge is all about keeping things running smoothly, like a well-oiled machine. It’s like the “stream of consciousness” you see in James Joyce’s Dubliners , except instead of thoughts, it’s about processes and procedures.
Domain 6 Management MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge makes sure everything’s on track, from project planning to risk management, keeping the whole operation humming along like a finely tuned engine.
However, the effectiveness of leadership styles can vary depending on the team’s characteristics and the project context.
- Communication Strategies:Effective communication is crucial for successful team management. This involves active listening, clear and concise messaging, and regular feedback. Regular team meetings, one-on-one conversations, and communication tools can facilitate effective communication. The advantages include improved team cohesion, reduced misunderstandings, and increased transparency.
However, effective communication requires effort and can be challenging in large or geographically dispersed teams.
Decision-Making Techniques
Making sound decisions is essential for effective management. Several techniques can help managers navigate complex situations and arrive at informed decisions.
- Decision Trees:Decision trees are graphical representations of possible outcomes based on a series of decisions. They help managers analyze different scenarios, assess risks, and make informed choices. The advantages include structured decision-making, identification of potential risks, and improved clarity. However, decision trees can be complex to create and might not be suitable for all situations.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis:This technique involves evaluating the costs and benefits of different options to determine the most financially viable choice. It helps managers prioritize projects, allocate resources effectively, and make decisions that align with business objectives. The advantages include a structured approach to decision-making, clear justification for choices, and alignment with financial goals.
However, cost-benefit analysis can be time-consuming and might not fully capture all relevant factors.
- SWOT Analysis:SWOT analysis stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This technique helps managers identify internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. By understanding these factors, managers can make informed decisions that capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats.
The advantages include a comprehensive understanding of the situation, identification of key factors, and informed decision-making. However, SWOT analysis can be subjective and might not capture all relevant factors.
Performance Management Techniques
Performance management involves setting goals, providing feedback, and evaluating progress. It’s a continuous process that helps individuals and teams achieve their full potential.
- Goal Setting:Clear and specific goals provide direction and motivation for individuals and teams. The SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goal-setting framework is widely used to ensure goals are well-defined and achievable. The advantages include increased focus, improved motivation, and clear performance benchmarks.
However, setting realistic and achievable goals requires careful planning and consideration.
- Performance Reviews:Regular performance reviews provide an opportunity to assess progress, provide feedback, and identify areas for improvement. These reviews can be formal or informal, and they should be conducted in a constructive and supportive manner. The advantages include regular feedback, identification of development needs, and performance improvement.
However, performance reviews can be time-consuming and require careful preparation and communication.
- 360-Degree Feedback:This technique involves collecting feedback from multiple sources, including peers, supervisors, and subordinates. It provides a comprehensive view of an individual’s performance and identifies areas for development. The advantages include a holistic perspective on performance, identification of blind spots, and enhanced self-awareness.
However, 360-degree feedback can be time-consuming and requires careful implementation to ensure anonymity and confidentiality.
Book Review: Domain 6 Management in Practice
This book review delves into the practical aspects of Domain 6 Management, analyzing its strengths and weaknesses, and highlighting its relevance to the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge.
Strengths of the Book
The book’s strengths lie in its practical approach to Domain 6 Management, providing real-world examples and case studies to illustrate key concepts. It effectively bridges the gap between theory and practice, making it a valuable resource for professionals seeking to apply Domain 6 principles in their daily work.
Domain 6 Management in the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge is all about keeping things running smoothly, like a well-oiled machine. You gotta know how to manage those projects, keep track of the budget, and make sure everyone’s on the same page.
It’s kinda like how the story in “Aline la Gloria Por el Infierno 25 Años Después (Spanish Edition)” Aline la Gloria Por el Infierno 25 Años Después (Spanish Edition) unfolds – you’ve got to keep up with all the twists and turns to stay in the game.
So, when you’re mastering Domain 6, you’re not just learning about management, you’re learning how to navigate the wild world of business like a true boss.
Weaknesses of the Book
Despite its strengths, the book has some weaknesses. One area for improvement is the lack of in-depth coverage of certain advanced topics within Domain 6 Management. Additionally, the book could benefit from a more comprehensive discussion of emerging trends and technologies impacting the field.
Key Takeaways and Relevance to the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge
The book provides valuable insights into the importance of effective management within the context of Domain 6. It emphasizes the need for clear communication, collaboration, and accountability among team members to achieve project goals. The book’s key takeaways align with the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge, reinforcing the principles of project management, risk assessment, and stakeholder engagement.
Examples and Data
The book includes several real-world examples of successful Domain 6 management practices. For instance, it highlights the case of a software development company that implemented a collaborative project management methodology, resulting in improved team communication and increased project efficiency. The book also provides data on the impact of effective management on project outcomes, demonstrating the positive correlation between strong leadership and successful project delivery.
Last Word
So, are you ready to level up your management skills and become a true champion of Domain 6 Management within the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge? This is your chance to gain the knowledge and insights you need to confidently lead, inspire, and achieve incredible results.
It’s time to unlock your full potential and dominate the MARKENDIUM SMPS landscape. Game on!
FAQ Resource
What is the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge?
The MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge is a comprehensive framework that Artikels the essential knowledge, skills, and practices required for success in the MARKENDIUM SMPS industry. It’s like the official rulebook for the game!
Why is Domain 6 Management so important?
Domain 6 Management is crucial because it provides the structure and guidance for effectively managing projects, resources, and teams within the MARKENDIUM SMPS context. It’s the foundation for efficient and successful operations.
How does Domain 6 Management relate to other domains within the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge?
Domain 6 Management is interconnected with all other domains within the MARKENDIUM SMPS Body of Knowledge. It provides the framework for applying knowledge and skills from other domains to achieve optimal outcomes.
What are some common challenges faced in Domain 6 Management?
Common challenges include resource allocation, team communication, project deadlines, and managing expectations. Domain 6 Management provides the tools and techniques to overcome these hurdles.