Lectern woodworking plans set the stage for crafting a beautiful and functional stand, perfect for presentations, speeches, or even adding a touch of elegance to your home library. Whether you’re a seasoned woodworker or just starting out, these plans provide a step-by-step guide to building your own lectern, from selecting materials to adding unique design elements.
This comprehensive guide explores the history of lecterns, delves into essential woodworking techniques, and offers detailed plans for various styles. You’ll learn about different lectern designs, the importance of ergonomics, and how to customize your creation with personalized touches. Get ready to bring your woodworking skills to life with a project that combines functionality and artistry.
Introduction to Lecterns
Lecterns, those elevated platforms with a slanted surface, have a long and rich history, playing a crucial role in communication and presentation across various settings. From ancient times to the modern era, lecterns have served as essential tools for speakers, educators, and religious leaders.
History and Purpose of Lecterns
Lecterns have been used for centuries, evolving alongside human communication practices. Their origins can be traced back to ancient Greece and Rome, where they were primarily used for reading aloud scrolls and texts. In the Middle Ages, lecterns became an integral part of religious ceremonies, serving as platforms for reading scriptures and delivering sermons.
Types of Lecterns and Their Uses
Lecterns come in a wide variety of designs, each tailored to specific uses and settings. Here are some common types:
- Pulpit Lecterns: Found in churches and other religious institutions, these lecterns are typically large and ornate, often featuring elaborate carvings and decorations. They are designed to elevate the speaker and create a sense of authority and reverence.
- Podium Lecterns: Commonly used in schools, universities, and public speaking events, these lecterns are generally smaller and more minimalist. They provide a stable platform for speakers to hold notes and maintain a professional appearance.
- Tabletop Lecterns: Smaller and more portable than other types, tabletop lecterns are ideal for use in classrooms, conference rooms, and other settings where space is limited. They can be easily moved and adjusted to suit the speaker’s needs.
- Modern Lecterns: Contemporary lecterns often feature sleek and minimalist designs, incorporating materials like glass, metal, and acrylic. They are designed to complement modern architectural styles and technology.
Significance of Lecterns in Communication and Presentation
Lecterns play a significant role in enhancing communication and presentation effectiveness. They provide a focal point for the speaker, allowing them to maintain eye contact with the audience and project their voice clearly. The slanted surface of the lectern allows speakers to refer to notes or visual aids without having to constantly turn away from the audience.
Woodworking Basics for Lecterns

Building a lectern is a rewarding woodworking project that requires basic skills and tools. This section will introduce essential woodworking tools and techniques, provide a basic lectern design, and guide you through the construction process.
Essential Woodworking Tools and Equipment
A well-equipped workshop is essential for building a lectern. The following tools and equipment are recommended:
- Table Saw: Used for making accurate cuts in wood.
- Miter Saw: Used for making precise angled cuts.
- Circular Saw: Used for making straight cuts in wood, particularly for large pieces.
- Hand Planer: Used for smoothing and leveling wood surfaces.
- Router: Used for creating decorative edges, grooves, and dadoes.
- Drill Press: Used for drilling precise holes in wood.
- Clamps: Used for holding wood pieces together during assembly.
- Sandpaper: Used for smoothing wood surfaces.
- Measuring Tape: Used for accurate measurements.
- Level: Used to ensure that the lectern is level.
- Safety Glasses: Always wear safety glasses when working with woodworking tools.
- Dust Mask: Protect yourself from sawdust.
- Ear Protection: Wear ear protection when using loud power tools.
Fundamental Woodworking Techniques
Woodworking involves various techniques that are essential for building a lectern.
- Cutting: Cutting wood accurately is essential for creating the components of the lectern. Use a table saw, miter saw, or circular saw to make straight and angled cuts.
- Joining: Wood pieces can be joined together using various techniques, such as:
- Dowel Joints: Used for joining two pieces of wood at a right angle. Dowels are inserted into holes drilled in both pieces of wood.
- Pocket Holes: A quick and easy way to join two pieces of wood at a right angle. Pocket holes are drilled at an angle into one piece of wood, allowing screws to be inserted from the side.
- Mortise and Tenon Joints: A strong and traditional joint used for joining two pieces of wood at a right angle. A mortise (rectangular hole) is cut into one piece of wood, and a tenon (rectangular projection) is cut into the other.
- Glue: Wood glue is essential for joining wood pieces together. Apply a thin, even coat of glue to the surfaces that will be joined.
- Finishing: Finishing a lectern involves applying a protective coating to the wood surface. This can be done with:
- Paint: Provides a durable and colorful finish.
- Stain: Enhances the natural grain of the wood.
- Varnish: Provides a protective layer over the wood surface.
Basic Lectern Structure
A basic lectern design can be constructed using plywood or solid wood.
Dimensions
- Height: 40-45 inches (101-114 cm)
- Width: 20-24 inches (51-61 cm)
- Depth: 16-18 inches (41-46 cm)
Materials
- Plywood: 3/4-inch (1.9 cm) thick plywood is a good choice for the lectern’s base and top.
- Solid Wood: Hardwoods such as oak, maple, or cherry can be used for the lectern’s legs, frame, and top.
- Wood Glue: Use a high-quality wood glue for joining the lectern’s components.
- Wood Screws: Use screws that are long enough to securely fasten the lectern’s components.
- Finish: Choose a finish that complements the wood and provides a protective layer.
Construction Steps
- Cut the components: Cut the plywood or solid wood to the desired dimensions using a table saw, miter saw, or circular saw.
- Assemble the base: Join the plywood or solid wood pieces to create the lectern’s base. Use dowel joints, pocket holes, or mortise and tenon joints. Secure the joints with wood glue and screws.
- Attach the legs: Attach the legs to the base using dowel joints, pocket holes, or mortise and tenon joints. Secure the joints with wood glue and screws.
- Attach the top: Attach the top to the frame using dowel joints, pocket holes, or mortise and tenon joints. Secure the joints with wood glue and screws.
- Finish the lectern: Sand the lectern’s surfaces smooth. Apply a finish of your choice.
Lectern Design and Construction
Lectern design and construction are multifaceted aspects that involve careful consideration of both aesthetic appeal and practical functionality. The lectern, often a focal point in presentations and speeches, should seamlessly blend form and function, ensuring comfort and ease of use for the speaker.
Lectern Styles and Features, Lectern woodworking plans
The design of a lectern is often influenced by its intended purpose and the overall aesthetic of the space where it will be used. Several styles exist, each offering distinct advantages and characteristics.
- Traditional Lecterns: These classic lecterns are typically characterized by a sturdy, upright structure with a sloped top surface for holding notes or books. They often feature decorative elements like carvings, moldings, or ornate legs. Examples include the “Cathedral Lectern” with its intricate carvings and the “Renaissance Lectern” with its elegant, flowing lines. These styles are often found in churches, libraries, or academic settings, where they lend a sense of formality and tradition.
- Modern Lecterns: In contrast to traditional styles, modern lecterns prioritize simplicity and clean lines. They often feature minimalist designs with sleek, geometric shapes. Materials like metal, acrylic, or even recycled materials are frequently used, offering a contemporary aesthetic. These lecterns are commonly found in corporate offices, conference rooms, or modern auditoriums, where they complement contemporary interiors.
- Portable Lecterns: Designed for mobility, portable lecterns are lightweight and compact. They often feature adjustable heights and folding designs for easy transport and storage. These lecterns are ideal for speakers who frequently travel or present in different locations. Portable lecterns are often made from lightweight materials like aluminum or plastic, making them easy to carry.
Ergonomics and Functionality
Ergonomics plays a crucial role in lectern design, ensuring comfort and ease of use for the speaker. A well-designed lectern promotes proper posture, reduces strain on the neck and shoulders, and allows for natural movement.
- Adjustable Height: The lectern’s height should be adjustable to accommodate speakers of different heights. A lectern that is too high can strain the neck, while one that is too low can lead to slouching. The optimal height allows for a relaxed posture with the speaker’s elbows at a 90-degree angle.
- Stable Base: A stable base is essential for preventing the lectern from tipping over, especially during dynamic presentations. A wide base provides a secure foundation, while strategically placed weights can further enhance stability. The base should also be designed to avoid tripping hazards and allow for easy movement.
- Reading Surface: The reading surface should be angled to ensure optimal visibility of notes or presentations. A slight incline helps reduce glare and promotes a natural head position. The surface should also be large enough to accommodate necessary materials without feeling cramped.
- Microphone Placement: If a microphone is used, its placement should be carefully considered. Ideally, the microphone should be positioned close to the speaker’s mouth without interfering with their movement or obstructing their view. A microphone boom arm or a built-in microphone stand can provide flexibility and convenience.
Decorative Elements and Embellishments
While functionality is paramount, decorative elements can add visual interest and enhance the aesthetic appeal of a lectern. These embellishments can range from subtle details to more elaborate designs, depending on the desired style.
- Carvings and Inlays: Traditional lecterns often feature intricate carvings and inlays, adding depth and texture to the design. These details can be inspired by historical motifs, floral patterns, or geometric designs. For example, a lectern might feature carvings of biblical scenes, floral patterns, or intricate geometric designs.
- Paint and Finish: The choice of paint and finish can significantly impact the lectern’s aesthetic. A traditional lectern might be painted in a rich, dark color like mahogany or walnut, while a modern lectern might feature a sleek, metallic finish or a bright, contemporary color. The finish should complement the overall design and the surrounding environment.
- Metalwork: Metal accents like brass or bronze can add a touch of elegance and sophistication. These accents can be incorporated into the lectern’s legs, handles, or decorative elements. Metalwork can be polished for a shiny finish or left in a raw state for a more rustic look.
- Lighting: Incorporating lighting can enhance the lectern’s visibility and create a dramatic effect. A spotlight directed at the speaker’s face can highlight their presence, while subtle lighting beneath the reading surface can illuminate notes and presentations. Lighting can also be used to create visual interest and highlight decorative elements.
Lectern Construction Plans: Lectern Woodworking Plans
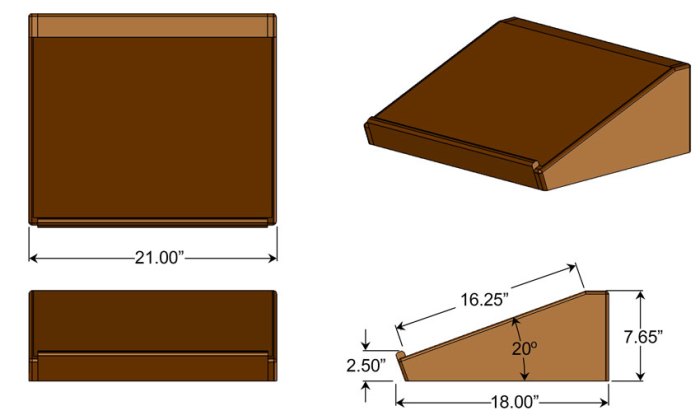
This section will provide you with a comprehensive guide to building a lectern from scratch. We’ll cover everything from selecting the right materials to assembling and finishing your masterpiece. You’ll find detailed plans, diagrams, and measurements for each component, ensuring a smooth and successful construction process.
Lectern Design Considerations
Before you start building, it’s essential to consider the design of your lectern. Factors to consider include:
- Size and Dimensions: Determine the appropriate height and width for your lectern based on its intended use and the space available. Consider the height of the user and the size of the materials you’ll be using.
- Style and Aesthetics: Choose a style that complements your personal preferences and the overall design of your space. Consider the type of wood, finish, and any decorative elements you want to incorporate.
- Functionality: Determine the specific features you need, such as a shelf for books, a microphone stand, or a light. Ensure the design accommodates these features.
Materials and Tools
To build a lectern, you’ll need the following materials and tools:
- Wood: Choose a durable and attractive hardwood like oak, maple, or cherry. Consider the thickness and quality of the wood for optimal stability and durability.
- Hardware: You’ll need screws, bolts, nuts, hinges, and other hardware to secure the different components of the lectern.
- Wood Glue: Use a high-quality wood glue to bond the various pieces together.
- Finishing Supplies: Select a finish that complements the wood and your desired aesthetic. Options include stain, paint, varnish, or polyurethane.
- Tools: You’ll need basic woodworking tools such as a saw, drill, sander, and measuring tape. Consider investing in a router and a table saw for more precise cuts.
Lectern Construction Steps
Here is a step-by-step guide to building a lectern:
- Cut the Wood: Use your saw to cut the wood to the dimensions specified in the plans. Ensure your cuts are accurate and square.
- Assemble the Base: Construct the base of the lectern by joining the legs and the bottom shelf using screws and wood glue. Make sure the base is sturdy and level.
- Create the Lectern Top: Cut and shape the top of the lectern to your desired dimensions. You may want to use a router to create a smooth and finished edge.
- Attach the Top: Secure the top to the base using screws and wood glue. Ensure the top is properly aligned and level.
- Add Shelves or Features: If your design includes additional shelves or features, cut and assemble them according to the plans. Attach them to the lectern using screws and wood glue.
- Sand and Finish: Once the lectern is assembled, sand it smooth using sandpaper of increasing grit. Apply your chosen finish according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Lectern Component Plans
This section provides detailed plans and diagrams for each component of the lectern. Use these plans as a guide for cutting, assembling, and finishing your lectern.
Base Plans
- Diagram: [Description of the base diagram: a rectangle with four legs attached at the corners, with dimensions for the width, length, and height of the base. The diagram can be labeled with dimensions for the legs, shelf, and other components. You can also include a note about the type of wood to be used for the base.]
- Measurements: [List of specific measurements for each component of the base, including the width, length, and thickness of the legs, shelf, and other components. You can also include a note about the type of wood to be used for the base.]
- Assembly Instructions: [Detailed instructions on how to assemble the base, including the use of screws, wood glue, and other hardware. You can also include tips on ensuring the base is sturdy and level.]
Top Plans
- Diagram: [Description of the top diagram: a rectangular or curved top with dimensions for the width, length, and thickness of the top. You can also include a note about the type of wood to be used for the top.]
- Measurements: [List of specific measurements for the top, including the width, length, and thickness. You can also include a note about the type of wood to be used for the top.]
- Assembly Instructions: [Detailed instructions on how to assemble the top, including the use of screws, wood glue, and other hardware. You can also include tips on ensuring the top is properly aligned and level.]
Shelf Plans (if applicable)
- Diagram: [Description of the shelf diagram: a rectangular or curved shelf with dimensions for the width, length, and thickness of the shelf. You can also include a note about the type of wood to be used for the shelf.]
- Measurements: [List of specific measurements for the shelf, including the width, length, and thickness. You can also include a note about the type of wood to be used for the shelf.]
- Assembly Instructions: [Detailed instructions on how to assemble the shelf, including the use of screws, wood glue, and other hardware. You can also include tips on ensuring the shelf is properly aligned and level.]
Assembly and Finishing
Once all the components are cut and assembled, it’s time to finish your lectern.
- Sanding: Sand the entire lectern using sandpaper of increasing grit to create a smooth surface. This will ensure a uniform finish and eliminate any imperfections.
- Finishing: Apply your chosen finish according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Consider using a stain to enhance the natural beauty of the wood or a paint to create a unique look. You can also use a varnish or polyurethane to protect the wood from scratches and spills.
- Hardware Installation: Install any necessary hardware, such as hinges, handles, or microphone stands. Make sure the hardware is securely attached and functional.
- Final Touches: Add any decorative elements or personalize your lectern with custom details. Consider adding a nameplate, engraving, or decorative accents to enhance its aesthetic appeal.
Lectern Customization and Variations
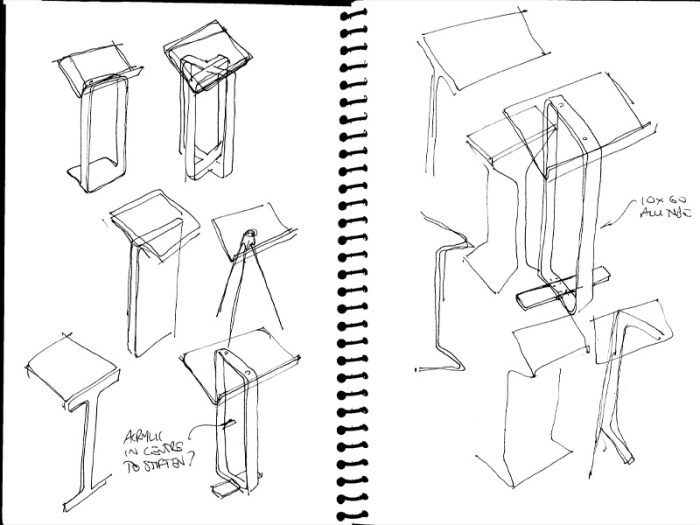
Your lectern is more than just a platform for speaking; it’s a reflection of your style and the message you want to convey. By exploring different materials, finishes, and integrated features, you can create a lectern that’s as unique as you are.
Customizing Materials and Finishes
Choosing the right materials and finishes can significantly impact your lectern’s look and feel.
- Wood Species: Explore various wood species like oak, cherry, maple, walnut, or mahogany. Each wood has unique grain patterns and colors, contributing to the lectern’s aesthetic appeal. For instance, oak offers durability and a classic look, while walnut provides rich, dark tones.
- Finishes: Consider stain colors, varnishes, or even paint to achieve the desired effect. A natural oil finish highlights the wood’s grain, while a lacquered finish provides a glossy, protective layer.
- Metal Accents: Incorporate metal accents like brass, copper, or stainless steel for a touch of elegance. These accents can be used for hinges, handles, or decorative elements.
Lecterns with Integrated Features
Adding integrated features to your lectern can enhance its functionality and make it more convenient to use.
- Storage Compartments: Build in drawers, shelves, or compartments for storing notes, books, or other essential items. This keeps your lectern organized and allows you to easily access materials during presentations.
- Lighting: Incorporate LED lights to illuminate your notes or enhance the lectern’s visual appeal. You can choose from various lighting styles, including spotlights, ambient lighting, or even adjustable reading lamps.
- Technology Integration: Consider adding a built-in microphone, speaker system, or even a tablet holder for seamless integration with technology. This can enhance your presentations and make them more engaging.
Lecterns for Specific Purposes and Styles
Lecterns can be tailored to suit various purposes and styles.
- Modern Lecterns: These lecterns often feature clean lines, minimalist designs, and contemporary materials like acrylic or metal. They can be used for modern presentations or in settings with a minimalist aesthetic.
- Traditional Lecterns: Traditional lecterns often have ornate carvings, classic wood finishes, and a more formal design. They are ideal for ceremonies, religious events, or settings with a historical or traditional feel.
- Portable Lecterns: For presentations on the go, consider a portable lectern that’s lightweight and easy to transport. These lecterns can be made from materials like lightweight plywood or aluminum.
Safety and Maintenance
Building a lectern is a rewarding project, but safety should always be a priority. This section covers essential safety precautions during construction and use, along with maintenance practices to ensure your lectern lasts for years to come.
Safety Precautions During Construction
- Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris, especially when using power tools.
- Use ear protection when operating loud machinery. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can damage your hearing.
- Ensure the work area is well-lit and free of clutter. A cluttered workspace increases the risk of accidents.
- Use appropriate tools for the job. Using the wrong tool can be dangerous and can also damage the materials.
- Never operate power tools when you are tired or under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
- Always disconnect power tools from the power source before making adjustments or changing blades.
- Keep your fingers away from the blade path of power tools.
- Use a clamp or vise to secure the workpiece when cutting or sanding.
- Always use a dust mask when working with wood. Wood dust can be harmful to your respiratory system.
Safety Precautions During Use
- Inspect the lectern regularly for any signs of damage or wear. Damaged or worn components should be repaired or replaced immediately.
- Make sure the lectern is stable and secure before using it. A wobbly lectern can be dangerous and could cause the lectern to fall over.
- Use a sturdy, non-slip mat under the lectern to prevent it from sliding on the floor.
- Avoid overloading the lectern. Overloading can cause the lectern to collapse or become unstable.
- Be careful when moving the lectern. Lifting it improperly can lead to injury.
Maintenance Practices
- Dust the lectern regularly with a soft cloth to remove dust and debris.
- Clean the lectern with a mild soap and water solution if needed.
- Apply a wood polish or sealant to protect the finish and enhance its appearance.
- Inspect the lectern’s hardware regularly for signs of wear or loosening. Tighten any loose screws or bolts.
- If the lectern has a shelf, make sure it is securely attached to the lectern.
- Store the lectern in a dry, well-ventilated area to prevent moisture damage.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
- Wobbly lectern: Check the legs for any signs of damage or looseness. Tighten any loose screws or bolts. If the legs are damaged, they will need to be replaced.
- Loose shelf: Check the shelf’s attachment points for any signs of loosening. Tighten any loose screws or bolts. If the shelf is still loose, it may need to be reattached or replaced.
- Scratched or damaged finish: Sand down the scratched area with fine-grit sandpaper. Apply a wood filler to fill in any deep scratches. Apply a new coat of wood finish to match the existing finish.
Concluding Remarks
With the right tools, materials, and a little dedication, you can build a stunning lectern that reflects your personal style and serves a practical purpose. Whether you’re using it for professional presentations, home decor, or simply enjoying the satisfaction of creating something unique, these woodworking plans provide a rewarding journey. So grab your tools, choose your wood, and get ready to create a masterpiece that stands the test of time.
FAQs
What types of wood are best for building a lectern?
Hardwoods like oak, maple, cherry, and walnut are popular choices due to their durability and attractive grain patterns. Softwoods like pine or cedar can also be used, but they may require additional finishing to protect them from scratches.
What are the most important safety precautions to consider during lectern construction?
Always wear safety glasses, ear protection, and a dust mask when working with power tools. Use clamps to secure your workpieces and take your time to avoid rushing or making mistakes.
How can I add storage compartments to my lectern?
You can incorporate shelves, drawers, or even a hidden compartment within the lectern design. Consider the size and shape of the lectern and the types of items you want to store.
Lecturn woodworking plans can be a great starting point for building your own unique piece, but if you want something truly special, you might want to consider custom woodworking. A skilled craftsperson can work with you to design a lectern that perfectly fits your needs and style, from the wood selection to the intricate details.
Whether you’re looking for a traditional design or something more modern, custom woodworking allows you to create a truly unique and personal piece.

