Medieval furniture plans offer a fascinating window into the past, allowing us to recreate the craftsmanship and artistry of a bygone era. These plans not only provide blueprints for building functional pieces but also offer insights into the materials, techniques, and design philosophies that shaped medieval life.
From sturdy chests and tables to elaborate beds and chairs, medieval furniture played a vital role in everyday life. These pieces were not just practical but also reflected the status and wealth of their owners. The plans reveal the meticulous attention to detail, the use of durable woods like oak and walnut, and the skilled handwork that went into creating these enduring pieces.
Introduction to Medieval Furniture

Medieval furniture, spanning from the 5th to the 15th centuries, played a vital role in daily life and reflects the evolving social and cultural landscape of the era. While often perceived as austere and simple, medieval furniture encompassed a diverse range of styles and designs, adapting to the changing needs and tastes of the period.
Medieval furniture construction relied heavily on readily available materials, with wood being the primary choice. Oak, pine, and elm were commonly used for their durability and strength. Other materials included iron, leather, and textiles, which were incorporated into functional and decorative elements.
Medieval Furniture Styles
Medieval furniture styles evolved significantly over the centuries, influenced by regional variations, technological advancements, and changing societal trends. Early medieval furniture, influenced by Roman and Germanic traditions, tended to be functional and robust. As the medieval period progressed, furniture became more elaborate and decorative, reflecting the growing prosperity and sophistication of society.
Key Medieval Furniture Styles
- Romanesque (9th-12th centuries): This style is characterized by sturdy construction, simple forms, and often features geometric designs and carvings. Examples include trestle tables, chests, and benches.
- Gothic (12th-15th centuries): This style is known for its pointed arches, intricate tracery, and emphasis on verticality. Furniture from this period often features elaborate carvings, stained glass, and painted decorations.
- Renaissance (14th-16th centuries): This style marked a transition from the Gothic era, incorporating classical elements and a renewed interest in humanism and naturalism. Furniture became more refined and elegant, with a focus on comfort and functionality.
Materials Used in Medieval Furniture
The materials used in medieval furniture construction were dictated by availability and practicality.
Common Materials
- Wood: Oak, pine, and elm were the most common woods used for furniture. Oak was prized for its strength and durability, while pine and elm were more readily available and affordable. Wood was often used for structural components, frames, and surfaces.
- Iron: Iron was used for hinges, locks, and other metalwork. It was also used for decorative elements such as nails, rivets, and studs. Iron was often forged and shaped to create intricate designs.
- Leather: Leather was used for upholstery, covering, and decorative accents. It was also used for straps, buckles, and other functional elements. Leather was often treated with dyes and finishes to create various colors and patterns.
- Textiles: Textiles were used for upholstery, curtains, and other decorative elements. Wool, linen, and silk were common fabrics used in medieval furniture. Textiles were often woven or embroidered with intricate designs.
Craftsmanship and Techniques
Medieval furniture makers were highly skilled artisans who employed a range of techniques to create durable and functional pieces.
Craftsmanship Techniques
- Woodworking: Medieval furniture makers used a variety of woodworking tools, including hand saws, chisels, planes, and hammers. They employed joinery techniques such as mortise and tenon joints, dovetail joints, and lap joints to create strong and lasting connections. They also used techniques such as carving, turning, and inlay to create decorative elements.
- Metalwork: Medieval metalworkers used techniques such as forging, casting, and engraving to create metalwork elements for furniture. They often incorporated intricate designs and decorative motifs into their work. Forging involved heating and shaping metal with hammers and anvils, while casting involved pouring molten metal into molds. Engraving involved carving designs into metal surfaces.
- Textile Arts: Medieval weavers and embroiderers created textiles that were used for upholstery, curtains, and other decorative elements. They employed a variety of techniques, including weaving, spinning, and embroidery. Weaving involved interlacing threads to create fabric, while spinning involved twisting fibers into yarn. Embroidery involved stitching decorative designs onto fabric.
Types of Medieval Furniture: Medieval Furniture Plans
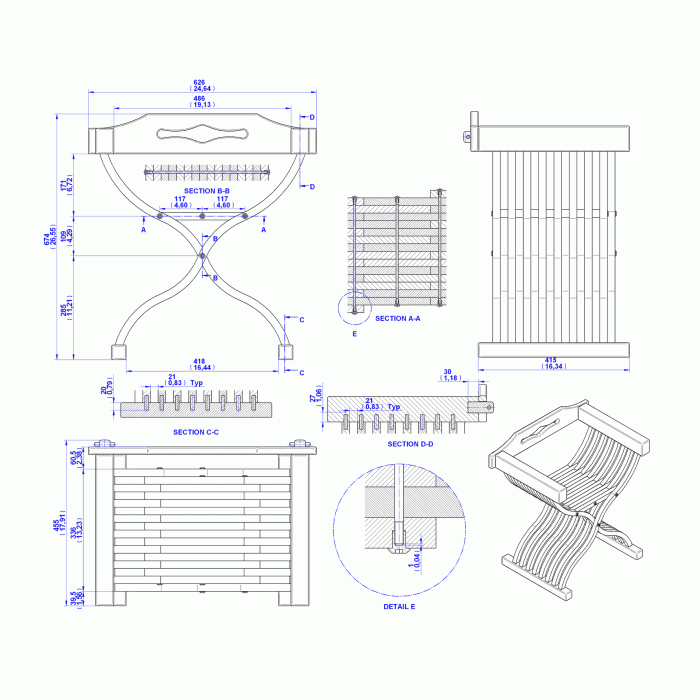
Medieval furniture was a reflection of the time’s social structure and the craftsmanship of the period. While often simple in design, it served practical purposes and displayed the wealth and status of its owners.
Medieval Furniture Types
Medieval furniture was generally crafted from wood, often oak or pine, and was typically designed for durability and functionality. Here is a table outlining some of the most common types of medieval furniture:
| Type | Description | Typical Uses | Design Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chest | A large, rectangular box with a hinged lid. | Storage for clothing, bedding, and other household items. | Often decorated with carvings, metal hardware, and paint. |
| Bed | A raised platform with a mattress and bedding. | Sleeping and resting. | Could be simple or elaborate, with headboards, footboards, and canopies. |
| Table | A flat surface supported by legs. | Eating, working, and writing. | Could be round, square, or rectangular, with varying heights and designs. |
| Chair | A seat with a back and legs. | Sitting. | Could be simple stools or more elaborate armchairs with carved backs and armrests. |
| Bench | A long, narrow seat without a back. | Seating for multiple people. | Often used in dining halls and churches. |
| Coffer | A small, chest-like container. | Storage for valuables and personal items. | Often made of wood and adorned with metal accents. |
| Trellis | A framework of interwoven slats. | Used for support and decoration. | Often used in gardens and for dividing spaces. |
| Wardrobe | A tall, freestanding cabinet with doors. | Storage for clothing and other personal items. | Often made of wood and decorated with carvings, metal hardware, and paint. |
Design Features and Variations
Medieval furniture was often characterized by its simple, functional designs.
- Carving: Carving was a common decorative element, often featuring geometric patterns, floral motifs, and religious imagery.
- Metal Hardware: Metal hardware, such as hinges, locks, and handles, was often used to enhance the functionality and appearance of furniture.
- Paint: Furniture was often painted in vibrant colors, such as red, blue, and green.
Variations in furniture styles were influenced by regional and temporal factors. For example, furniture from the Romanesque period (10th-12th centuries) tended to be more robust and simple, while furniture from the Gothic period (12th-16th centuries) was more ornate and elaborate.
Furniture Styles of Different Medieval Eras
Medieval furniture styles evolved over time, reflecting changes in social, economic, and technological factors.
- Romanesque Period (10th-12th centuries): Romanesque furniture was characterized by its simple, functional designs. It was typically made of sturdy wood and often featured heavy carvings and metal hardware. Examples include chests, beds, and tables.
- Gothic Period (12th-16th centuries): Gothic furniture was more ornate and elaborate than Romanesque furniture. It often featured pointed arches, intricate carvings, and delicate tracery. Examples include elaborate beds with canopies and richly carved chairs.
- Renaissance Period (14th-16th centuries): The Renaissance saw a revival of classical art and architecture, which influenced furniture design. Renaissance furniture was often characterized by its symmetry, proportion, and use of classical motifs. Examples include chests with classical ornamentation and chairs with padded seats and backs.
Medieval Furniture Plans and Construction
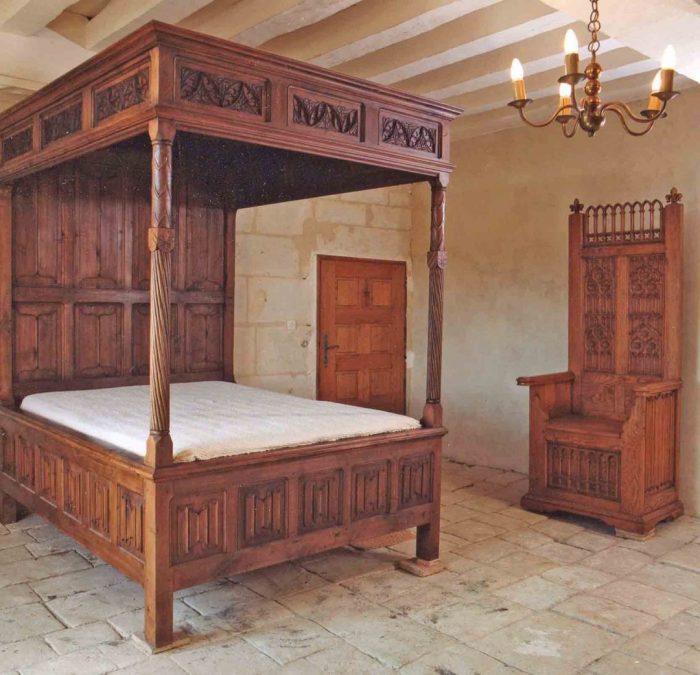

Medieval furniture plans were crucial for the successful creation of functional and aesthetically pleasing pieces. They served as blueprints, guiding craftspeople through the process of building furniture. These plans ensured consistency, accuracy, and efficiency in the construction process.
Common Methods and Tools for Creating Furniture Plans, Medieval furniture plans
Furniture plans were created using various methods and tools. The most common methods included:
- Freehand sketching: This method involved drawing the furniture design directly onto a surface, such as a piece of parchment or wood. The craftsman would use a pencil, charcoal, or ink to create the Artikel of the furniture, along with any details like joinery and ornamentation. This method was prevalent during the early Middle Ages when formal drafting techniques were less common.
- Geometric constructions: As mathematical knowledge advanced, craftsmen began using geometric constructions to create more precise plans. This method involved using a compass, ruler, and protractor to create accurate measurements and angles. This method was particularly helpful for complex designs involving curves and intricate details.
- Templates: Templates were used to create repetitive shapes and patterns in furniture designs. They were made from wood, metal, or other materials and were used to trace the desired shape onto the furniture piece. Templates were especially helpful for creating furniture with intricate carvings, mouldings, or decorative elements.
The tools used for creating furniture plans included:
- Rulers: These were used to measure lengths and distances accurately.
- Compasses: Compasses were used to draw circles and arcs, essential for creating curves and decorative elements.
- Protractors: Protractors were used to measure angles, ensuring accurate joinery and construction.
- Pens and pencils: These were used to draw the plans and mark measurements on the materials.
Examples of Historical Furniture Plans and Their Interpretations
Many historical furniture plans have survived to this day, offering valuable insights into medieval furniture construction techniques. One example is the “Plan for a Chest” from the 14th century, found in the British Museum. This plan details the dimensions, joinery, and ornamentation of a chest, providing a detailed guide for its construction.
Another example is the “Plan for a Bed” from the 15th century, found in the Victoria and Albert Museum. This plan shows the construction of a four-poster bed, including the frame, headboard, footboard, and canopy. It also illustrates the use of mortise-and-tenon joinery, a common technique in medieval furniture construction.
These historical plans allow us to understand how medieval craftsmen approached furniture design and construction. They reveal the importance of precision, planning, and the use of specialized tools and techniques.
Building Medieval Furniture
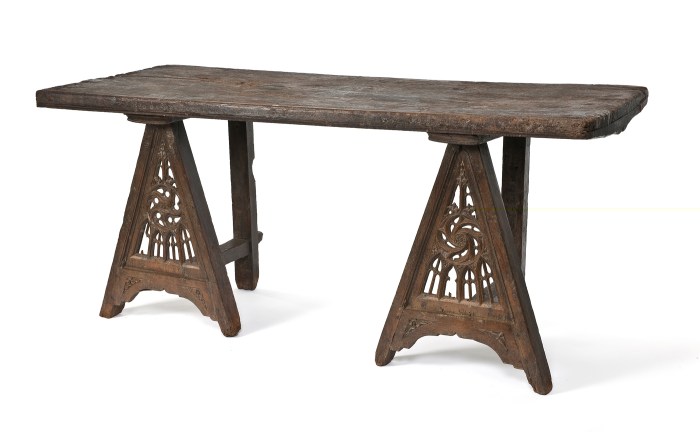

Bringing medieval furniture plans to life is a rewarding experience, blending historical accuracy with practical woodworking skills. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to constructing a simple medieval furniture piece, focusing on traditional tools and techniques.
Choosing a Project
Starting with a simple project is essential for beginners. A stool or small table is an excellent choice, requiring fewer complex joints and allowing you to practice basic woodworking skills. The project should align with your skill level and available tools.
Gathering Materials
Medieval furniture relied heavily on locally sourced materials. Oak, ash, and pine were common choices for their strength and durability. Softwoods like pine were often used for less-stressed parts, while hardwoods like oak provided structural support.
Preparing the Wood
Before construction, the wood must be properly prepared. This involves planing the wood to create smooth, flat surfaces, ensuring consistent thickness and removing any knots or imperfections.
Cutting and Joining
Medieval joinery techniques relied on simple but effective methods like mortise and tenon joints. A mortise is a rectangular hole cut into one piece of wood, while a tenon is a projecting piece that fits into the mortise.
To cut a mortise, a chisel and mallet are used to remove wood from the mortise’s interior. A tenon is created by cutting a shoulder and a cheek on the end of the wood piece.
Assembling the Furniture
Once the individual pieces are cut and joined, they are assembled using traditional methods. Medieval furniture relied on pegs or wooden dowels to secure joints. These methods, though simple, provide strong and durable bonds.
Finishing Touches
After assembly, the furniture is often sanded smooth and finished with a natural oil or wax. This protects the wood from moisture and adds a beautiful sheen.
Medieval Furniture in Modern Settings
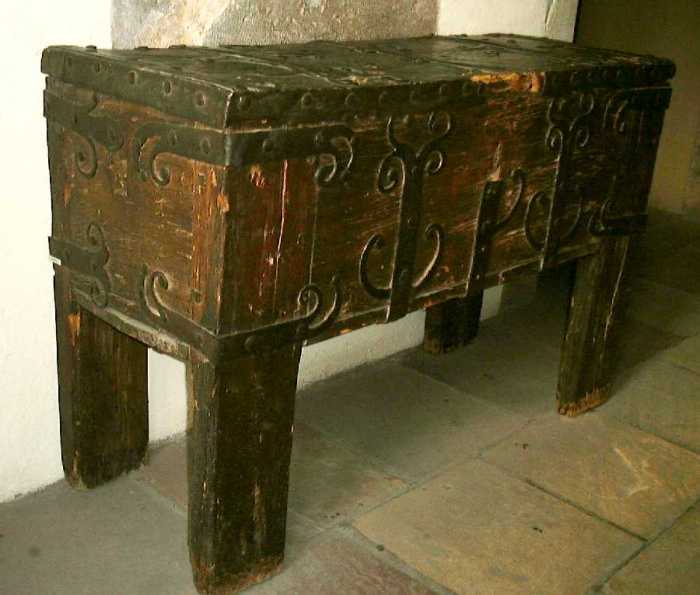

Medieval furniture designs, despite their historical context, possess a timeless appeal that continues to resonate with modern sensibilities. Their robust construction, intricate details, and functional elegance make them a compelling choice for contemporary interiors. This section delves into the enduring relevance of medieval furniture in modern settings, exploring how contemporary furniture makers incorporate medieval elements into their designs and the aesthetic and historical significance of integrating these pieces into modern spaces.
Examples of Medieval Furniture Elements in Modern Designs
Modern furniture makers often draw inspiration from medieval furniture, incorporating elements like hand-carved details, sturdy construction, and the use of natural materials into their contemporary designs. This blend of historical aesthetics and modern functionality creates pieces that are both visually striking and practical.
- Hand-Carved Details: Contemporary furniture makers often use hand-carving techniques to create intricate patterns and designs, reminiscent of the elaborate ornamentation found on medieval furniture. These carvings add a touch of history and craftsmanship to modern pieces, creating a unique and visually captivating aesthetic.
- Sturdy Construction: Medieval furniture was built for durability, using solid wood and robust joinery techniques. Modern furniture makers often employ similar construction methods, ensuring that their pieces are not only beautiful but also long-lasting. This focus on quality and longevity aligns with the values of sustainability and responsible consumption prevalent in modern design.
- Natural Materials: Medieval furniture was primarily crafted from natural materials like wood, leather, and metal. Modern furniture makers continue to utilize these materials, often sourcing them sustainably and incorporating them into their designs in innovative ways. The use of natural materials adds warmth, texture, and a sense of authenticity to modern spaces.
Last Point
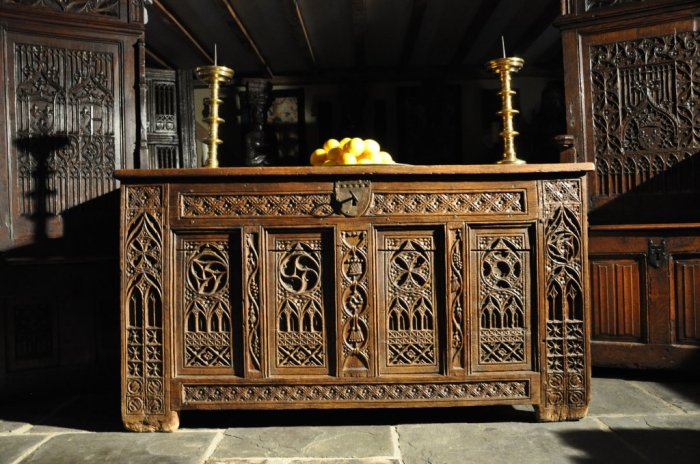

By studying medieval furniture plans, we gain a deeper appreciation for the ingenuity and artistry of past generations. These plans serve as a valuable resource for both historians and craftspeople, allowing us to connect with the past and bring its beauty and functionality into the present. Whether you’re a seasoned woodworker or a curious beginner, exploring the world of medieval furniture plans offers a rewarding journey into history and craftsmanship.
Detailed FAQs
What tools were commonly used in medieval furniture construction?
Medieval furniture makers relied on hand tools such as chisels, planes, saws, hammers, and mallets. They also used specialized tools like joinery planes, mortise and tenon cutters, and carving tools.
Where can I find medieval furniture plans?
You can find medieval furniture plans in historical archives, museums, and online databases. Many books and websites dedicated to woodworking and historical crafts also feature plans.
Are medieval furniture plans difficult to follow?
The complexity of medieval furniture plans varies. Some plans are relatively simple, while others require advanced woodworking skills. It’s essential to choose a plan that matches your experience level.
Medieval furniture plans offer a glimpse into a bygone era, showcasing craftsmanship and functionality. If you’re looking for unique woodworking projects that go beyond the ordinary, you might find inspiration in these historical designs. Unique woodworking projects can be a great way to explore new techniques and bring a touch of history into your home.
From sturdy trestle tables to intricate chests, medieval furniture plans offer a wealth of possibilities for the woodworker seeking a challenge.
