Plans for building furniture are the foundation of any successful woodworking project. Whether you’re a seasoned craftsman or a curious beginner, having a detailed plan ensures a smooth and rewarding experience. From selecting the right materials to mastering essential construction techniques, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to create beautiful and functional furniture pieces.
This guide delves into the intricate world of furniture making, providing a comprehensive overview of each step involved. From initial design concepts to the final finishing touches, you’ll learn about the essential tools, techniques, and materials that are key to crafting quality furniture.
Planning & Design
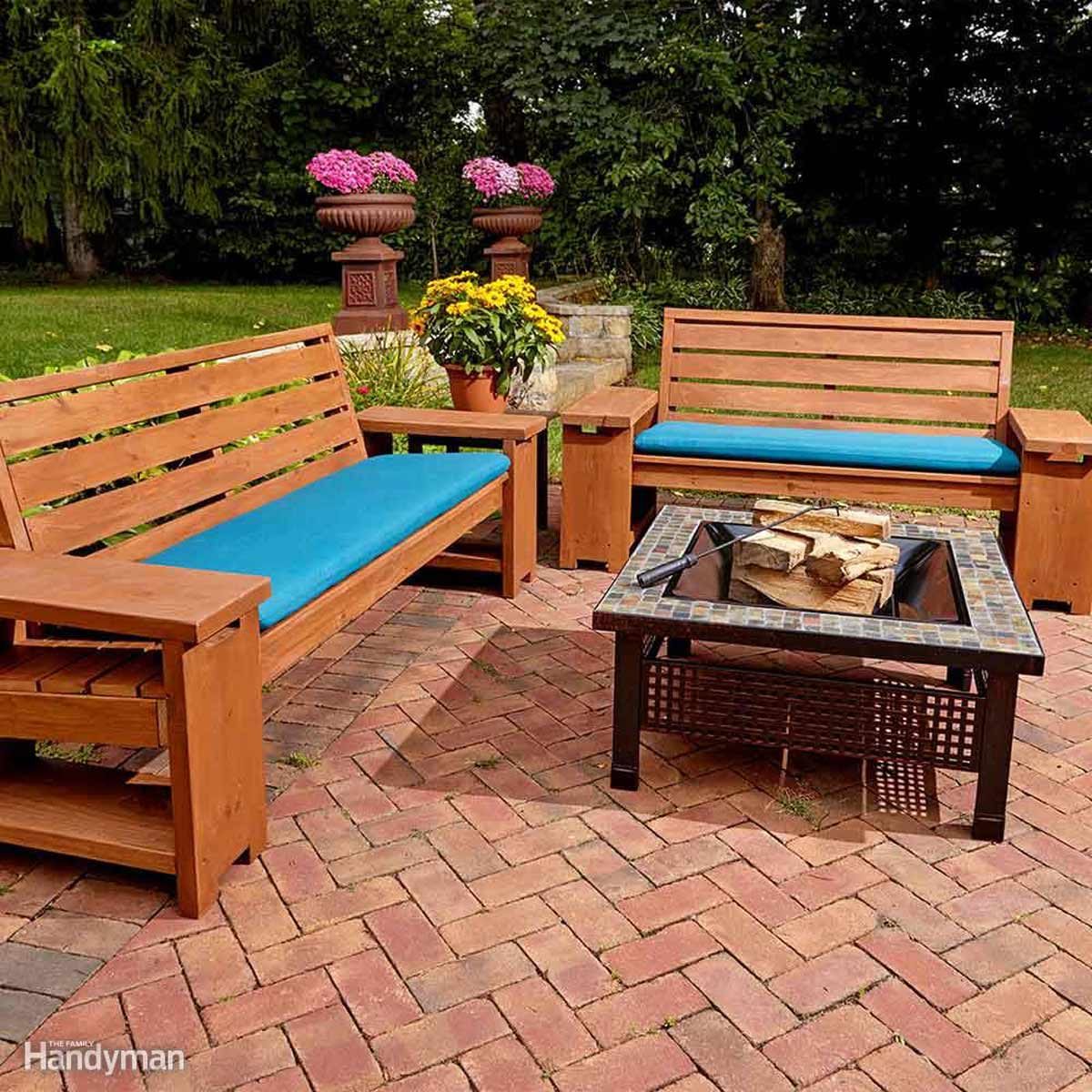

Planning and design are crucial steps in any furniture project. A well-thought-out plan will save you time, materials, and frustration in the long run.
Software and Tools
Using software or drawing tools for furniture design offers numerous benefits. These tools provide a visual representation of your project, allowing you to experiment with different designs and dimensions. They also help you create accurate measurements, calculate material requirements, and generate detailed assembly instructions.
Furniture Design Elements
Furniture design involves understanding and incorporating various elements.
Joints
Joints are crucial for connecting different pieces of wood. Common furniture joints include:
- Mortise and Tenon: A strong and traditional joint where a tenon (a projection on one piece) fits into a mortise (a hole in the other piece).
- Dovetail: A strong and decorative joint used for joining two pieces of wood at a right angle, typically used for drawer fronts.
- Rabbet: A groove cut into the edge of a board, used for joining boards together.
- Dado: A groove cut across the width of a board, used for fitting a panel or shelf.
- Butt Joint: A simple joint where two pieces of wood are butted together, often reinforced with glue and screws.
Construction Techniques
Construction techniques determine the overall stability and durability of your furniture.
- Frame and Panel: A common construction method where a frame is built around a panel, often used for doors and tabletops.
- Box Construction: A method where all sides are joined together to form a box, typically used for cabinets and drawers.
- Dowel Construction: A simple method where dowels are used to connect pieces of wood, often used for chairs and tables.
Finishes
Finishes enhance the appearance and durability of your furniture.
- Paint: A versatile finish that offers a wide range of colors and textures.
- Stain: A finish that penetrates the wood and enhances its natural grain patterns.
- Varnish: A clear finish that protects the wood from scratches and moisture.
- Wax: A finish that provides a protective layer and enhances the shine of the wood.
Creating a Furniture Plan
Creating a detailed plan is essential for a successful furniture project.
Step 1: Define the Project
Clearly define the purpose, style, and dimensions of your furniture. Consider the intended use, desired aesthetic, and available space.
Step 2: Gather Measurements
Take accurate measurements of the space where the furniture will be placed. Determine the desired dimensions for the piece, including height, width, and depth.
Step 3: Choose Materials
Select the appropriate materials based on your design, budget, and desired durability. Consider factors such as wood type, thickness, and finish.
Step 4: Create a Sketch or Drawing
Create a rough sketch or drawing of the furniture, including all dimensions and details. This will help you visualize the final product and identify potential issues early on.
Step 5: Develop Detailed Plans
Use software or drawing tools to create detailed plans with accurate measurements, material lists, and assembly instructions. Include diagrams for each joint and construction technique.
Step 6: Create a Cutting List
Generate a cutting list that specifies the size and quantity of each piece of wood needed for your project.
Step 7: Prepare the Materials
Cut and prepare all the materials according to your cutting list. Ensure all pieces are accurately sized and ready for assembly.
Step 8: Assemble the Furniture
Follow your assembly instructions carefully, using appropriate tools and techniques. Pay attention to alignment, joint strength, and overall stability.
Step 9: Apply Finish
Once the furniture is assembled, apply the desired finish. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for each product.
Material Selection
Choosing the right materials is crucial for building furniture that is both aesthetically pleasing and durable. The material you select will significantly impact the final look, feel, and longevity of your project.
Types of Wood for Furniture Making
Wood is a popular choice for furniture due to its natural beauty, versatility, and durability. There are numerous wood species available, each with unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications.
- Hardwoods: Hardwoods are generally denser and stronger than softwoods, making them ideal for furniture that needs to withstand heavy use. Examples include oak, maple, cherry, walnut, and mahogany.
- Softwoods: Softwoods are typically lighter and less expensive than hardwoods, making them suitable for projects that require less strength. Examples include pine, fir, cedar, and spruce.
Comparing Wood Species
When choosing wood for furniture, it is important to consider its properties, such as hardness, grain pattern, and durability.
- Hardness: Hardness refers to the wood’s resistance to indentation and scratching. Hardwoods like oak and maple are highly resistant to wear and tear, while softer woods like pine are more susceptible to damage.
- Grain Pattern: The grain pattern refers to the arrangement of wood fibers, which can significantly affect the wood’s appearance. Some woods, like oak, have a pronounced grain pattern, while others, like maple, have a more subtle grain.
- Durability: Durability refers to the wood’s ability to withstand decay, insects, and moisture. Some woods, like cedar and redwood, are naturally resistant to decay, while others, like pine, are more susceptible to damage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Other Materials
While wood is a popular choice for furniture, other materials, such as metal, plastic, and glass, offer unique advantages and disadvantages.
- Metal: Metal is strong, durable, and resistant to damage. It is often used for furniture frames, legs, and hardware. However, metal can be heavy and prone to rust.
- Plastic: Plastic is lightweight, affordable, and easy to clean. It is often used for chairs, tables, and storage units. However, plastic can be easily scratched and damaged.
- Glass: Glass is elegant and adds a modern touch to furniture. It is often used for tabletops, shelves, and doors. However, glass can be fragile and prone to breakage.
Selecting the Right Materials for Your Project, Plans for building furniture
When selecting materials for your furniture project, consider the following factors:
- Style: The style of your furniture will dictate the materials you choose. For example, a rustic style might call for wood, while a modern style might call for metal or glass.
- Budget: The cost of materials will vary depending on the type and quality of the wood, metal, or plastic you choose.
- Desired Lifespan: If you want your furniture to last for many years, you will need to choose durable materials.
Tools & Equipment: Plans For Building Furniture
Having the right tools and equipment is crucial for building furniture. The tools you need will depend on the type of furniture you’re building and your level of experience. However, there are some essential tools that every furniture builder should have.
Hand Tools
Hand tools are essential for many furniture building tasks, from measuring and marking to cutting and shaping wood. They are often more precise and versatile than power tools, making them ideal for delicate work.
- Measuring Tools:
- Tape Measure: A tape measure is essential for measuring the dimensions of your furniture pieces and materials. Choose a tape measure with a durable metal blade and a locking mechanism to keep it secure.
- Ruler: A ruler is helpful for smaller measurements and for checking the accuracy of your cuts. Look for a ruler with clear markings and a durable construction.
- Try Square: A try square is used to check the squareness of your cuts and to mark right angles. Look for a try square with a sturdy blade and a sharp edge.
- Combination Square: A combination square combines a ruler and a try square, making it a versatile tool. Look for a combination square with a sturdy blade and a clear scale.
- Marking Tools:
- Pencil: A pencil is used to mark the wood before cutting. Choose a pencil with a sharp point and a durable lead.
- Marking Gauge: A marking gauge is used to mark parallel lines on the wood. Look for a marking gauge with a sturdy base and a sharp point.
- Scriber: A scriber is used to mark lines on the wood. Look for a scriber with a sharp point and a comfortable handle.
- Cutting Tools:
- Hand Saw: A hand saw is used to cut wood. Choose a hand saw with a sharp blade and a comfortable handle.
- Backsaw: A backsaw is used to make precise cuts in wood. Look for a backsaw with a sharp blade and a sturdy frame.
- Coping Saw: A coping saw is used to cut intricate shapes in wood. Look for a coping saw with a sharp blade and a comfortable handle.
- Chisel: A chisel is used to shape and carve wood. Choose a chisel with a sharp blade and a comfortable handle.
- Plane: A plane is used to smooth and flatten wood. Look for a plane with a sharp blade and a comfortable handle.
- Joining Tools:
- Hammer: A hammer is used to drive nails and other fasteners. Choose a hammer with a comfortable grip and a durable head.
- Screwdriver: A screwdriver is used to drive screws. Choose a screwdriver with a comfortable grip and a durable shaft.
- Clamps: Clamps are used to hold pieces of wood together while they are being glued or joined. Choose clamps with a strong grip and a durable construction.
- Wrench: A wrench is used to tighten and loosen nuts and bolts. Choose a wrench with a comfortable grip and a durable construction.
- Finishing Tools:
- Sandpaper: Sandpaper is used to smooth the surface of wood. Choose sandpaper with a variety of grits to achieve different levels of smoothness.
- Sanding Block: A sanding block is used to hold sandpaper and make it easier to sand. Choose a sanding block with a comfortable grip and a durable construction.
- Brush: A brush is used to apply paint, stain, and other finishes to wood. Choose a brush with a soft bristle and a comfortable handle.
- Roller: A roller is used to apply paint and stain to large surfaces. Choose a roller with a durable frame and a soft roller cover.
Power Tools
Power tools can greatly speed up the furniture building process and allow you to accomplish tasks that would be difficult or impossible with hand tools alone.
- Circular Saw: A circular saw is used to cut wood quickly and accurately. Choose a circular saw with a powerful motor and a durable blade.
- Jigsaw: A jigsaw is used to cut curved shapes in wood. Choose a jigsaw with a powerful motor and a variety of blades.
- Router: A router is used to shape and trim wood. Choose a router with a powerful motor and a variety of bits.
- Drill: A drill is used to drill holes in wood. Choose a drill with a powerful motor and a variety of drill bits.
- Belt Sander: A belt sander is used to smooth and shape large surfaces of wood. Choose a belt sander with a powerful motor and a durable belt.
- Random Orbit Sander: A random orbit sander is used to smooth and polish wood. Choose a random orbit sander with a powerful motor and a durable sanding pad.
Safety Gear
Safety gear is essential for protecting yourself from injury while building furniture.
- Safety Glasses: Safety glasses protect your eyes from flying debris. Choose safety glasses with a comfortable fit and a clear lens.
- Hearing Protection: Hearing protection is important for protecting your ears from the loud noise of power tools. Choose hearing protection that fits comfortably and provides adequate noise reduction.
- Dust Mask: A dust mask is important for protecting your lungs from wood dust. Choose a dust mask with a tight seal and a high-quality filter.
- Work Gloves: Work gloves protect your hands from splinters and other hazards. Choose work gloves with a comfortable fit and a durable construction.
Investing in Quality Tools
Investing in quality tools is important for several reasons. First, quality tools are more durable and will last longer. Second, quality tools are more precise and will help you create better furniture. Third, quality tools are safer to use and will help you avoid injury.
Investing in quality tools is an investment in your furniture building skills and your safety.
Construction Techniques
Construction techniques play a crucial role in building sturdy and aesthetically pleasing furniture. They involve various methods for joining, assembling, and finishing pieces, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. Understanding these techniques is essential for achieving the desired outcome and ensuring the longevity of your furniture project.
Joinery Methods
Joinery methods are techniques used to connect wood pieces together, providing strength and stability to the furniture structure. These methods range from simple to complex, offering different levels of strength and aesthetic appeal.
- Mortise and Tenon: This traditional joinery technique involves creating a rectangular hole (mortise) in one piece of wood and a corresponding projection (tenon) on the other. The tenon fits snugly into the mortise, forming a strong and durable joint. It is often used for sturdy furniture pieces like tables and chairs.
- Dovetail: A dovetail joint is known for its strength and intricate appearance. It involves creating interlocking “tails” and “pins” on the mating surfaces of the wood pieces. The tapered shape of the dovetails creates a strong, interlocking joint that resists separation. This joint is commonly used for drawers and cabinet sides, adding both strength and visual appeal.
- Biscuit Joint: Biscuit joints are created using thin, oval-shaped biscuits that are inserted into slots cut into the wood. Glue is applied to the biscuits and the pieces are clamped together. This method is relatively quick and easy, making it suitable for joining large panels or flat surfaces.
- Pocket Hole Joinery: Pocket holes are created using a specialized jig that drills angled holes into the edge of a piece of wood. Screws are then driven into these holes, creating a strong and concealed joint. Pocket holes are commonly used for assembling cabinet boxes and other furniture pieces where the joint needs to be hidden.
Assembly Techniques
Assembly techniques involve putting the individual components of a furniture piece together using various methods.
- Gluing: Glue is a common method for joining wood pieces together, providing a strong and permanent bond. Wood glue is applied to the mating surfaces of the wood pieces, which are then clamped together until the glue dries.
- Screwing: Screws are used to fasten wood pieces together, offering a secure and durable joint. They are commonly used in conjunction with glue, providing additional strength and stability.
- Nailing: Nails are a quick and easy way to fasten wood pieces together, although they are not as strong as screws or glue. They are often used for temporary or decorative purposes.
Finishing Techniques
Finishing techniques are applied to the surface of the furniture to enhance its appearance, protect it from damage, and provide a smooth and durable finish.
- Sanding: Sanding is essential for creating a smooth and even surface before applying any finish. It involves using sandpaper of various grits to remove imperfections and create a consistent texture.
- Staining: Staining is used to change the color of the wood without obscuring its natural grain. Stains are available in a wide range of colors and finishes, allowing you to achieve the desired look for your furniture.
- Painting: Painting is a versatile finishing technique that can be used to completely cover the wood surface with a solid color. Paints are available in a variety of colors and finishes, offering endless possibilities for customization.
Furniture Styles
Furniture styles are a reflection of the times in which they were created, often reflecting the social, economic, and artistic trends of the era. Understanding different furniture styles can help you choose the right look for your projects and inspire your own designs.
Traditional Furniture Styles
Traditional furniture styles are characterized by their classic and timeless designs, often featuring intricate details, rich materials, and a sense of history.
- Victorian: Popular in the late 19th century, Victorian furniture is known for its ornate carvings, dark woods, and heavy, elaborate designs. Iconic pieces include the chaise lounge, the grandfather clock, and the claw-foot bathtub.
- Edwardian: A transition style between Victorian and Art Deco, Edwardian furniture is characterized by simpler lines, lighter woods, and a more streamlined aesthetic. Examples include the wingback chair, the writing desk, and the dining table with a pedestal base.
- Queen Anne: Popular in the early 18th century, Queen Anne furniture is known for its elegant curves, cabriole legs, and walnut wood. Examples include the Queen Anne chair, the dressing table, and the bookcase.
- Georgian: Characterized by its symmetry, balance, and refined elegance, Georgian furniture was popular in the 18th century. Examples include the Chippendale chair, the chest of drawers, and the secretary desk.
Contemporary Furniture Styles
Contemporary furniture styles are characterized by their clean lines, simple forms, and modern materials. These styles often embrace functionality and minimalist aesthetics.
- Mid-Century Modern: Popular in the 1950s and 1960s, Mid-Century Modern furniture is known for its organic shapes, geometric forms, and use of materials like plywood and plastic. Iconic pieces include the Eames Lounge Chair, the Barcelona Chair, and the Noguchi Coffee Table.
- Scandinavian: Characterized by its minimalist design, light woods, and functional forms, Scandinavian furniture emphasizes simplicity and natural materials. Examples include the Arne Jacobsen Egg Chair, the Panton Chair, and the String Shelving System.
- Industrial: Industrial furniture styles often feature exposed metal, reclaimed wood, and a raw, unfinished aesthetic. Examples include the Tolix Chair, the Wassily Chair, and the Brooklyn Bridge Lamp.
Rustic Furniture Styles
Rustic furniture styles are characterized by their use of natural materials, rough textures, and handcrafted details. These styles often evoke a sense of warmth, comfort, and connection to nature.
- Country: Country furniture styles often feature distressed wood, painted finishes, and simple, functional designs. Examples include the farmhouse table, the ladder-back chair, and the rocking chair.
- Log Cabin: Log cabin furniture is characterized by its use of logs and rustic finishes. Examples include the log bed frame, the log coffee table, and the log bench.
- Shaker: Shaker furniture is known for its simple, functional designs, clean lines, and use of natural materials like wood and maple. Examples include the Shaker chair, the Shaker table, and the Shaker cupboard.
Sustainability & Eco-Friendly Practices
Building furniture sustainably is not just a trend, it’s a responsible way to contribute to a healthier planet. By choosing eco-friendly materials and practices, we can minimize our impact on the environment while creating beautiful and durable pieces.
Benefits of Using Reclaimed or Recycled Wood
Reclaimed or recycled wood offers a range of benefits, making it a valuable choice for furniture building. It reduces the need for harvesting new trees, lessening deforestation and its associated environmental consequences. Using reclaimed wood also helps to preserve natural resources and reduce waste. The unique character and history embedded in reclaimed wood add a touch of authenticity and charm to furniture pieces.
Minimizing Waste and Maximizing Resource Efficiency
Efficient resource utilization is key to sustainable furniture building. Careful planning and precise cutting can significantly reduce waste.
- Measure twice, cut once.
- Use a cutting list to minimize material waste.
- Consider using scrap wood for smaller projects or decorative elements.
- Store leftover materials for future projects or donate them to local schools or community workshops.
Eco-Friendly Furniture Finishes and Coatings
Choosing eco-friendly finishes and coatings is essential for creating furniture that is both beautiful and sustainable.
- Natural oil finishes, such as tung oil, linseed oil, and walnut oil, offer a durable and protective coating while being free of harmful chemicals.
- Beeswax finishes provide a natural, water-resistant barrier, enhancing the wood’s natural beauty.
- Water-based paints and stains are low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) options, minimizing harmful emissions during application and drying.
Inspiration & Resources
Inspiration is the lifeblood of any creative endeavor, and furniture making is no exception. Whether you’re a seasoned craftsman or just starting out, exploring diverse sources of inspiration is crucial for developing your unique style and pushing your creative boundaries.
Inspiration from Renowned Designers and Craftspeople
Inspiration can be found in the work of master furniture designers and craftspeople. Their innovative techniques, use of materials, and aesthetic sensibilities can ignite your imagination and guide your own creative journey.
- Charles and Ray Eames: Known for their iconic designs like the Eames Lounge Chair and the Eames Molded Plastic Chair, they revolutionized furniture design with their focus on functionality, form, and innovative materials.
- Hans Wegner: This Danish designer is celebrated for his elegant and functional chairs, like the “Wishbone Chair” and the “Round Chair,” showcasing the beauty of simple forms and exquisite craftsmanship.
- George Nakashima: A renowned woodworker, Nakashima’s furniture embodies the spirit of nature, with his signature use of live-edge slabs and intricate joinery techniques. He believed in honoring the natural beauty of wood and creating pieces that were both functional and artistic.
- Eileen Gray: This Irish architect and designer is known for her pioneering work in modernism, particularly her furniture designs, which were characterized by sleek lines, geometric forms, and innovative materials.
Online Resources and Communities
The internet provides a wealth of resources for furniture makers, from online communities to dedicated websites. These platforms offer a space to connect with fellow enthusiasts, share knowledge, and find inspiration.
- Woodworking Forums: These online forums offer a platform for woodworkers to connect, share projects, ask questions, and learn from each other. Popular forums include LumberJocks, WoodworkingTalk, and The Wood Whisperer.
- YouTube Channels: Numerous YouTube channels are dedicated to woodworking and furniture making, providing tutorials, project ideas, and insights from experienced makers. Some popular channels include The Wood Whisperer, Paul Sellers, and Steve Ramsey.
- Instagram and Pinterest: These social media platforms are filled with stunning furniture designs, allowing you to discover new trends, explore different styles, and find inspiration for your own projects.
- Online Furniture Making Courses: Websites like Skillshare, Udemy, and Coursera offer a variety of online courses on furniture making, covering various techniques, styles, and design principles.
Seeking Inspiration from Various Sources
Inspiration can be found in unexpected places. Explore a wide range of sources to fuel your creativity.
- Books and Magazines: Architectural and design books and magazines can offer a wealth of inspiration, showcasing furniture from different eras and styles. Look for publications like “Dwell,” “Metropolis,” and “Architectural Digest.”
- Museums and Galleries: Visiting museums and galleries can provide a unique opportunity to experience furniture design firsthand. Explore exhibits featuring historical furniture, contemporary designs, and works by renowned designers.
- Nature: Nature is a boundless source of inspiration. Observe the shapes, textures, and patterns found in the natural world to inspire your furniture designs.
- Travel: Traveling to different cultures and countries can expose you to unique furniture styles and craftsmanship traditions. Observe how people live, the furniture they use, and the materials they incorporate into their homes.
Developing Your Own Unique Designs
Inspiration is the starting point, but it’s your creativity that will truly set your furniture designs apart. Don’t be afraid to experiment, blend different styles, and push the boundaries of traditional furniture making.
- Experiment with Materials: Explore a variety of materials beyond traditional wood, such as metal, glass, or recycled materials. Experiment with different textures, colors, and finishes to create unique and visually appealing pieces.
- Embrace Functionality: Consider the intended use of the furniture and design it with functionality in mind. Create pieces that are not only beautiful but also practical and comfortable.
- Tell a Story: Imbue your furniture designs with a story or a concept. Use materials, shapes, and colors to convey a particular mood or theme.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Fail: Failure is a part of the creative process. Don’t be discouraged by mistakes; learn from them and use them as opportunities to grow and improve.
End of Discussion
With a solid understanding of planning, material selection, tools, construction techniques, and furniture styles, you’ll be well-equipped to embark on your own furniture building journey. Remember, the key is to embrace the process, experiment with different designs, and find joy in creating something beautiful and functional with your own hands.
Questions and Answers
What are some common furniture styles?
Furniture styles vary widely, ranging from traditional (e.g., Victorian, Colonial) to modern (e.g., Mid-Century Modern, Scandinavian). Each style has unique characteristics and historical influences.
How do I choose the right wood for my furniture project?
Consider factors like hardness, grain pattern, durability, and budget. Hardwoods like oak and maple are durable and offer beautiful grain patterns, while softer woods like pine are easier to work with but may not be as robust.
What safety precautions should I take when working with power tools?
Always wear safety glasses, ear protection, and a dust mask. Use tools with appropriate guards and ensure they are in good working condition. Never operate tools while fatigued or under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
Building furniture is a rewarding hobby, and it all starts with a solid foundation. A well-built workbench is essential for any woodworker, and there are tons of great plans available online. Check out woodworking work bench plans for inspiration and detailed instructions.
Once you have your workbench set up, you’ll be ready to tackle any furniture project, from simple shelves to intricate tables.
