Woodworking project design sets the stage for crafting beautiful and functional pieces. It’s not just about the final product, but the journey of planning, visualizing, and bringing your ideas to life. From sketching initial concepts to choosing the right wood and tools, each step is crucial in ensuring a successful outcome. This guide delves into the fundamentals of woodworking project design, offering insights into the process, key considerations, and valuable resources to help you create your own masterpieces.
This guide explores the entire design process, from defining your project’s purpose and style to selecting materials, tools, and techniques. You’ll learn how to utilize design software, create detailed plans, and navigate potential challenges. Whether you’re a seasoned woodworker or a curious beginner, this comprehensive guide will empower you to transform your woodworking dreams into tangible reality.
Understanding Woodworking Project Design
Woodworking project design is the process of planning and creating a detailed blueprint for a woodworking project. It involves everything from conceptualizing the final product to selecting materials, tools, and techniques. A well-designed woodworking project is essential for a successful and enjoyable woodworking experience.
Importance of Planning and Design in Woodworking
Planning and design are crucial in woodworking as they provide a roadmap for the entire project. They help to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications, minimizes waste, and prevents costly mistakes. A well-defined plan also allows for efficient resource allocation and helps to stay on schedule.
Key Elements Influencing Successful Woodworking Project Design
Several key elements influence the success of woodworking project design.
Project Goals and Requirements
Project goals and requirements are the foundation of any successful woodworking project. Defining the purpose of the project, its intended use, and the desired aesthetic are essential. For example, a sturdy workbench for a workshop will have different design considerations than a delicate jewelry box.
Material Selection
Material selection is a critical aspect of woodworking project design. Factors to consider include the type of wood, its availability, cost, and suitability for the intended purpose. Different woods have unique properties such as hardness, grain pattern, and workability.
Construction Techniques
Construction techniques are the methods used to assemble the different components of the woodworking project. Choosing the right techniques is essential for achieving the desired strength, durability, and aesthetic. Some common construction techniques include joinery, glueing, and fastening.
Tool Selection
Tool selection is an integral part of woodworking project design. The right tools are essential for achieving the desired results and ensuring safety. Different tools are designed for specific tasks, and choosing the appropriate tool for each step is crucial.
Budget and Time Constraints
Budget and time constraints are important factors to consider during woodworking project design. Establishing a budget and timeframe helps to guide the project’s scope and ensure that the project remains feasible.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount in woodworking. The design should incorporate safety features to minimize the risk of accidents. This includes using appropriate tools, working in a well-lit and organized workspace, and wearing protective gear.
Aesthetics and Design
Aesthetics and design are important aspects of woodworking project design. The design should reflect the desired aesthetic and style, considering factors such as the overall shape, proportions, and finish.
Design Considerations
Designing a woodworking project involves more than just choosing a pattern and cutting wood. It requires careful consideration of various factors that will influence the final outcome, its usability, and its aesthetic appeal.
Design Styles
Design styles in woodworking encompass a wide range of aesthetic preferences and techniques. Understanding these styles can help you choose the best approach for your project, whether you’re building a classic piece of furniture or a modern sculpture.
- Traditional Styles: Traditional styles often emphasize craftsmanship, durability, and timeless elegance. They often feature intricate details, hand-carved elements, and use of natural wood finishes. Examples include Shaker, Arts and Crafts, and Victorian styles.
- Modern Styles: Modern styles prioritize clean lines, simplicity, and functionality. They often use geometric shapes, minimal ornamentation, and contemporary materials like metal and glass. Examples include Mid-Century Modern, Scandinavian, and Minimalist styles.
- Rustic Styles: Rustic styles embrace the natural beauty of wood, showcasing its knots, grain patterns, and imperfections. They often feature distressed finishes, reclaimed wood, and simple, functional designs. Examples include Farmhouse, Lodge, and Country styles.
- Contemporary Styles: Contemporary styles are characterized by their use of modern materials and techniques, often incorporating bold colors, geometric patterns, and unconventional shapes. They may feature a mix of traditional and modern elements, pushing the boundaries of design.
Impact of Materials Selection
The choice of wood significantly influences the design and construction of a woodworking project. Each type of wood possesses unique characteristics that affect its appearance, workability, and durability.
- Hardwoods: Hardwoods are generally denser and more durable than softwoods. They are often used for furniture, flooring, and structural elements. Examples include oak, maple, cherry, walnut, and mahogany. Hardwoods are known for their strength, durability, and beautiful grain patterns, but they can be more expensive and challenging to work with.
- Softwoods: Softwoods are generally lighter and less dense than hardwoods. They are often used for construction, framing, and plywood. Examples include pine, fir, spruce, and cedar. Softwoods are typically more affordable and easier to work with, but they may not be as durable or as visually appealing as hardwoods.
- Plywood: Plywood is a manufactured sheet material composed of thin layers of wood veneer glued together with alternating grain directions. This construction provides strength and stability, making it suitable for a wide range of woodworking projects. Plywood is often used for furniture, cabinets, and structural applications.
- MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard): MDF is a manufactured sheet material made from wood fibers that are bound together with resin. It is a smooth and dense material, making it ideal for intricate designs and smooth finishes. MDF is often used for furniture, cabinet doors, and moldings.
Functionality and Ergonomics
Functionality and ergonomics are crucial considerations in woodworking design. A well-designed project should be not only aesthetically pleasing but also practical and comfortable to use.
- Functionality: Functionality refers to the purpose and usability of a woodworking project. For example, a chair should be comfortable to sit in, a table should be sturdy and stable, and a cabinet should provide adequate storage space.
- Ergonomics: Ergonomics focuses on the relationship between humans and their working environment. In woodworking, it involves designing projects that are comfortable to use, minimize strain on the body, and promote safety. For example, a chair should have proper back support and armrests, a workbench should be at a comfortable height, and tools should be designed for easy grip and maneuverability.
Design Tools and Techniques

Designing a woodworking project involves translating your vision into a tangible plan. This plan serves as a blueprint for your project, guiding you through every step from material selection to final assembly. To achieve this, you need the right tools and techniques to effectively communicate your ideas.
Sketching
Sketching is a fundamental tool in woodworking design. It allows you to quickly capture your initial ideas and explore different possibilities. The act of drawing, even in a rough form, helps you visualize the project, identify potential issues, and refine your design.
“Sketching is a way of thinking on paper.” – Frank Ching
Drafting
Drafting involves creating detailed, precise drawings using drafting tools or software. This method is ideal for creating accurate measurements, ensuring all parts fit together seamlessly. It provides a clear visual representation of the project, making it easier to understand and execute.
3D Modeling
3D modeling software allows you to create a virtual representation of your project. This technology provides a highly realistic preview of the finished product, allowing you to identify any potential design flaws or issues before committing to the actual construction.
- Advantages: 3D modeling offers several benefits, including the ability to visualize the project from multiple angles, experiment with different materials, and even create realistic renderings.
- Disadvantages: 3D modeling software can be expensive and require a learning curve. It may not be suitable for simple projects, where sketching or drafting might be more efficient.
Software Tools
Numerous software tools are available for woodworking design, catering to various skill levels and project complexities. Some popular options include:
- SketchUp: A user-friendly 3D modeling software ideal for beginners and professionals.
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A powerful software for 3D modeling, CAD, and CAM, offering advanced features for complex projects.
- SolidWorks: A professional-grade 3D CAD software with a wide range of capabilities.
- Rhino 3D: A powerful software for surface modeling and design, commonly used for furniture and product design.
Project Planning and Execution
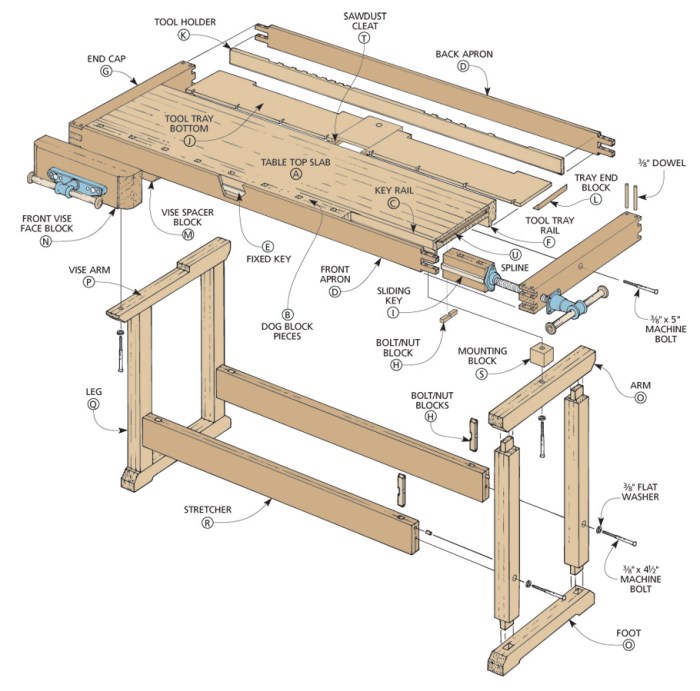
A well-structured plan is essential for a successful woodworking project. It helps you visualize the entire process, anticipate potential challenges, and ensure efficient use of your time and resources.
Creating a Detailed Project Plan, Woodworking project design
A detailed project plan Artikels every step of your woodworking journey, from initial design to final finishing. It serves as a roadmap, guiding you through the entire process and minimizing the risk of errors or omissions.
- Project Overview: Begin by defining the project’s scope, purpose, and desired outcome. Clearly articulate what you aim to achieve and the intended use of the finished product.
- Materials List: Create a comprehensive list of all materials needed, specifying quantities, types, and sources. Consider factors like wood species, dimensions, finishes, and hardware.
- Tool Inventory: Compile a list of tools required for each stage of the project, ensuring you have the necessary equipment and accessories.
- Step-by-Step Instructions: Break down the project into manageable steps, providing detailed instructions for each stage. Include diagrams, sketches, or photos to illustrate complex processes.
- Time Estimates: Assign realistic timeframes for each step, factoring in potential delays or unexpected challenges. This helps you manage your time effectively and stay on schedule.
- Budget: Estimate the overall project cost, considering materials, tools, and any additional expenses. This allows you to plan your budget and avoid unexpected financial burdens.
Preparing Materials and Tools
Once you have a detailed project plan, it’s time to gather your materials and tools. Proper preparation ensures a smooth and efficient execution of your project.
- Material Selection: Carefully choose materials that meet your project’s requirements, considering factors like wood species, quality, and availability.
- Material Preparation: Prepare your materials according to the project plan, ensuring they are cut, sanded, or finished as needed. This saves time during project execution.
- Tool Check and Maintenance: Inspect and maintain your tools before starting the project, ensuring they are in good working order and properly adjusted. This minimizes the risk of accidents or delays.
- Work Area Setup: Prepare your workspace, ensuring it is clean, well-lit, and organized. This creates a safe and efficient working environment.
Safety Measures During Project Execution
Safety should always be a top priority during woodworking projects. Taking precautions helps prevent accidents and ensures a safe working environment.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate safety gear, including eye protection, hearing protection, gloves, and dust masks, to minimize the risk of injuries.
- Tool Safety: Use tools correctly and follow manufacturer instructions. Never operate tools that are damaged or malfunctioning.
- Work Area Safety: Maintain a clean and organized workspace, removing clutter and ensuring adequate lighting.
- Fire Safety: Be aware of fire hazards, such as dust accumulation and the use of flammable materials. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
- Machine Safety: Use machines according to safety guidelines, always ensuring they are properly guarded and operated with caution.
Woodworking Project Design Challenges
Woodworking project design, while exciting, can present a range of challenges. From conceptualization to execution, numerous hurdles can arise, demanding creative problem-solving and a thorough understanding of the design process.
Understanding Common Design Challenges
Common woodworking project design challenges can be grouped into several categories:
- Material Selection and Usage: Choosing the right wood for a project is crucial. Wood species vary in hardness, grain patterns, and susceptibility to warping or cracking. Understanding these properties is vital to prevent material failure and achieve the desired aesthetic.
- Joint Design and Execution: Selecting and implementing the appropriate joints for your project is essential for structural integrity. Joints, such as mortise and tenon, dovetail, or butt joints, each have strengths and weaknesses that should be considered based on the project’s requirements.
- Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances: Achieving precise measurements and maintaining tolerances is critical for successful woodworking projects. Even small errors can lead to misaligned parts, gaps, or other issues that can compromise the project’s appearance and functionality.
- Aesthetic Design and Functionality: Balancing aesthetic appeal with functionality is a constant challenge. A beautiful design may not always be practical, and a functional design might not be visually appealing. Finding the right balance is crucial to create a successful project.
- Budget and Time Constraints: Budgetary limitations and time constraints can significantly impact design decisions. Finding cost-effective materials, optimizing design for efficiency, and managing project timelines are crucial for achieving a successful outcome.
Strategies for Overcoming Design Obstacles
Overcoming woodworking project design challenges requires a combination of planning, problem-solving, and resourcefulness. Here are some effective strategies:
- Thorough Planning and Preparation: A well-defined plan is the foundation for successful woodworking projects. Creating detailed drawings, considering material properties, and understanding joint types can prevent costly mistakes and ensure a smooth execution process.
- Experimentation and Prototyping: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different materials, techniques, and designs. Creating prototypes allows you to test your ideas, identify potential issues, and refine your approach before committing to the final project.
- Seeking Guidance and Support: Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from experienced woodworkers, online communities, or woodworking books and resources. Sharing your challenges and seeking advice can provide valuable insights and solutions.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Woodworking projects rarely go exactly as planned. Be prepared to adapt your design or approach if unforeseen challenges arise. Maintaining flexibility can help you overcome obstacles and achieve a satisfactory outcome.
Resources and Support for Design Challenges
Numerous resources and support systems are available to assist woodworkers in addressing design challenges:
- Online Communities and Forums: Websites like woodworking forums and social media groups provide a platform for sharing experiences, asking questions, and receiving advice from other woodworkers.
- Woodworking Books and Magazines: A vast library of woodworking literature offers guidance on various aspects of design, techniques, and troubleshooting.
- Woodworking Classes and Workshops: Hands-on workshops and classes provide practical experience and expert guidance on specific techniques and design concepts.
- Local Woodworking Clubs and Associations: Joining local woodworking clubs or associations offers opportunities for networking, sharing knowledge, and receiving support from fellow woodworkers.
Conclusion

With a solid understanding of woodworking project design, you’ll be equipped to tackle any project with confidence. Remember, the key is to approach each project with a well-defined plan, carefully chosen materials, and a touch of creativity. As you progress, you’ll find that the joy of woodworking lies not only in the finished product but also in the journey of creation itself. So, grab your tools, unleash your imagination, and let your woodworking journey begin!
FAQ Summary
What are some essential woodworking tools for beginners?
A basic set of tools for beginners includes a hand saw, measuring tape, hammer, screwdriver, drill, and sandpaper.
How do I choose the right wood for my project?
Consider the project’s purpose, desired appearance, and budget. Hardwoods like oak and maple are durable, while softwoods like pine are easier to work with.
Where can I find woodworking project plans online?
Popular websites for woodworking plans include Ana White, Woodworking for Mere Mortals, and Popular Woodworking.
What are some safety tips for woodworking?
Always wear safety glasses, use proper tools for the job, and avoid loose clothing.
Designing a woodworking project is like building a house – you need a solid foundation. That foundation is understanding the tools you’ll use. You wouldn’t build a house without a hammer and saw, right? The same goes for woodworking.
Learn about the different woodworking machines available and you’ll be able to design projects that push your skills and creativity.
