Workshop woodworking plans are your roadmap to crafting stunning and functional pieces. Whether you’re a seasoned woodworker or just starting out, these plans provide detailed instructions, material lists, and cutting diagrams to guide you through every step of the process. Imagine transforming raw lumber into a beautiful table, a sturdy bookshelf, or even a custom-built piece of furniture – all thanks to the clear guidance of woodworking plans.
This guide will delve into the world of workshop woodworking plans, covering everything from choosing the right plans for your skill level to mastering essential woodworking techniques. We’ll explore the benefits of using plans, discuss safety precautions, and offer tips for achieving professional-quality results.
Introduction to Workshop Woodworking Plans

Workshop woodworking plans are essential tools for any woodworker, whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out. They provide detailed instructions and diagrams that guide you through every step of the project, ensuring a successful outcome.
Using woodworking plans offers numerous benefits.
Benefits of Using Woodworking Plans
- Clear Instructions: Woodworking plans provide step-by-step instructions that eliminate confusion and ensure you understand each process.
- Accurate Measurements: Plans include precise measurements for every component, minimizing errors and ensuring proper fit.
- Material List: A detailed material list helps you purchase the exact materials needed, avoiding waste and unnecessary expenses.
- Visualization: Plans often include diagrams and illustrations that help you visualize the finished project and understand the construction process.
- Time Management: Woodworking plans provide an estimated timeline, helping you manage your time effectively and plan your project accordingly.
Types of Woodworking Plans
Woodworking plans come in various formats and cater to different skill levels and project complexities. Here are some common types:
- Beginner Plans: These plans are designed for novice woodworkers, featuring simple designs and easy-to-follow instructions. Examples include simple shelves, birdhouses, or small storage boxes.
- Intermediate Plans: These plans cater to woodworkers with some experience, offering more complex designs and techniques. Examples include furniture pieces like coffee tables, chairs, or small cabinets.
- Advanced Plans: These plans are for experienced woodworkers and involve intricate designs, demanding techniques, and specialized tools. Examples include custom-built furniture, architectural elements, or intricate wood carvings.
Plan Availability
You can find woodworking plans from various sources:
- Online Resources: Websites dedicated to woodworking offer a vast library of plans, ranging from free to paid options. Popular websites include Woodworking for Mere Mortals, Ana White, and The Wood Whisperer.
- Books and Magazines: Numerous woodworking books and magazines feature detailed plans and project ideas.
- Local Woodworking Stores: Many woodworking stores offer a selection of plans, both pre-printed and digital.
- Plan Services: Some companies specialize in creating custom woodworking plans tailored to your specific needs and preferences.
Choosing the Right Workshop Woodworking Plans
Choosing the right woodworking plans is crucial for a successful project. It ensures you have the necessary instructions and guidance to complete your project, from selecting the right materials to assembling the finished product.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Plans
Several factors influence the selection of woodworking plans. These factors are important for determining the project’s complexity, the materials required, and your overall woodworking experience.
- Project Complexity: Assess the level of difficulty and the amount of time required for the project. Beginners should start with simpler plans and gradually move towards more challenging ones.
- Skill Level: Choose plans that match your current woodworking skills. Don’t be afraid to start with beginner-friendly projects to build confidence and experience.
- Materials and Tools: Evaluate the types of materials and tools required for the project. Ensure you have access to the necessary equipment or are willing to invest in it.
- Plan Format: Consider the format of the plans. Some plans are available as digital downloads, while others are printed books or physical blueprints. Choose the format that best suits your needs and preferences.
- Plan Quality: Look for plans that are well-written, detailed, and easy to understand. High-quality plans often include step-by-step instructions, clear diagrams, and a list of materials.
- Customer Support: Check if the plan provider offers customer support in case you encounter any difficulties.
Comparing Plan Providers
When choosing a woodworking plan provider, consider the following aspects:
| Plan Provider | Plan Variety | Plan Quality | Price Range | Customer Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woodcraft | Extensive selection of plans for all skill levels | Detailed and well-written plans with clear diagrams | $10-$50 per plan | Excellent customer support through email and phone |
| Rockler | Wide range of plans, including furniture, toys, and home decor | High-quality plans with step-by-step instructions | $5-$30 per plan | Responsive customer support through email and live chat |
| Ana White | Free plans for various projects, including furniture and home decor | Easy-to-follow plans with clear instructions and diagrams | Free | Limited customer support, but a large online community for help |
| The Wood Whisperer | Detailed plans for furniture and other woodworking projects | High-quality plans with step-by-step instructions and videos | $10-$50 per plan | Excellent customer support through email and forum |
Plan Complexity and Skill Level
The complexity of woodworking plans is directly related to the required skill level. Beginners should choose plans that are easy to understand and follow, with simple instructions and diagrams. As you gain experience, you can gradually move towards more complex plans that require advanced techniques and tools.
It is essential to choose plans that match your current skill level. Don’t be afraid to start with beginner-friendly projects to build confidence and experience.
Understanding Workshop Woodworking Plans

Workshop woodworking plans are the blueprints for your projects, providing detailed instructions and diagrams to guide you through the construction process. They are essential for ensuring a successful outcome and minimizing mistakes.
Common Plan Elements
Woodworking plans typically include several key elements that help you understand the project and execute it accurately.
- Materials List: This list specifies the exact types and quantities of wood, hardware, and other materials needed for the project. It helps you gather everything before you start working, ensuring you have everything on hand.
- Cutting Diagrams: These diagrams illustrate the precise dimensions and angles of each piece of wood you need to cut. They help you cut the wood accurately, minimizing waste and ensuring proper fit during assembly.
- Assembly Instructions: These instructions provide step-by-step guidance on how to assemble the project, including the order of operations, joint types, and fastening techniques. They are crucial for understanding the construction process and avoiding mistakes.
Types of Woodworking Plans
There are various types of woodworking plans available, each catering to different skill levels and project complexities.
- Beginner Plans: These plans are designed for individuals with little to no woodworking experience. They typically feature simple designs, straightforward instructions, and common woodworking techniques.
- Intermediate Plans: These plans cater to woodworkers with some experience and a basic understanding of woodworking techniques. They may involve more complex designs, intricate joinery, and advanced techniques.
- Advanced Plans: These plans are for experienced woodworkers who are comfortable with challenging designs, intricate joinery, and specialized tools. They may involve custom designs, unique woodworking techniques, and high levels of precision.
Common Woodworking Joints
Woodworking plans often utilize various joints to connect pieces of wood securely and aesthetically.
- Butt Joint: This is the simplest joint, where two pieces of wood are joined end-to-end. It is suitable for basic projects but may require additional reinforcement for strength.
- Dado Joint: This joint involves cutting a groove (dado) in one piece of wood to accommodate the thickness of another piece. It creates a strong and flush connection.
- Mortise and Tenon Joint: This joint involves cutting a rectangular hole (mortise) in one piece of wood and a corresponding projection (tenon) on the other. It is a strong and durable joint, commonly used in furniture making.
- Dovetail Joint: This joint features interlocking tapered pins and slots that create a strong and visually appealing connection. It is often used in drawers and other furniture components.
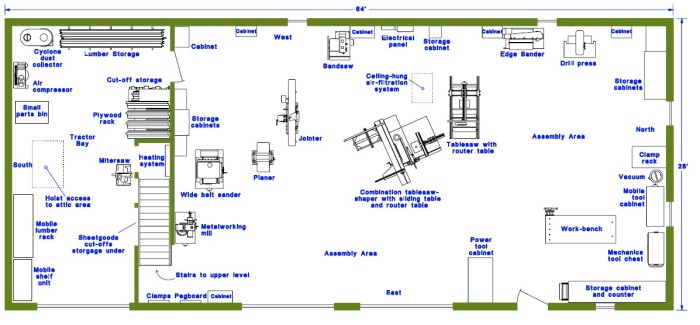
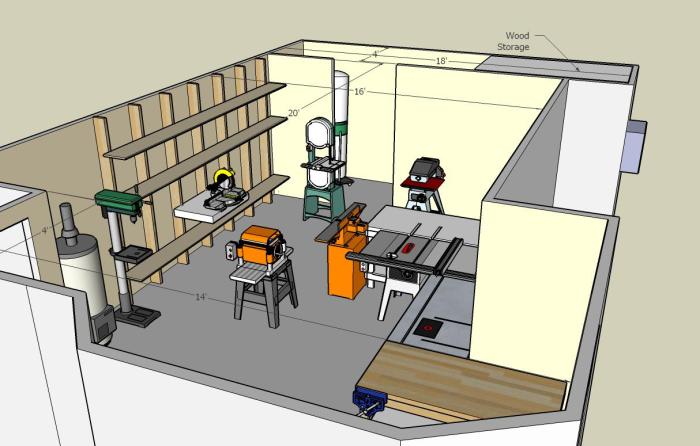
Workshop Setup and Safety
A well-organized and safe workshop is crucial for woodworking projects. It ensures efficient workflow and protects you from potential hazards. This section will guide you through setting up your workshop and implementing essential safety measures.
Essential Workshop Tools
Having the right tools is fundamental for woodworking. Here’s a checklist of essential tools for a well-equipped workshop:
- Hand Tools:
- Hammer
- Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead)
- Wrenches (adjustable and socket)
- Pliers (needle-nose and slip-joint)
- Chisels
- Mallet
- Clamps (various sizes)
- Measuring tape
- Level
- Pencil
- Utility knife
- Power Tools:
- Circular saw
- Jigsaw
- Drill/Driver
- Router
- Sander (belt and orbital)
- Table saw
- Planer
- Safety Equipment:
- Safety glasses
- Hearing protection
- Dust mask
- Work gloves
- First aid kit
Safety Precautions, Workshop woodworking plans
Woodworking involves inherent risks, so prioritizing safety is paramount. Here are essential safety precautions to follow:
- Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris.
- Use hearing protection when operating loud machinery.
- Wear a dust mask to prevent inhaling wood dust, which can be harmful to your lungs.
- Keep your workspace clean and organized to minimize tripping hazards.
- Use appropriate tools for the task and ensure they are in good working condition.
- Never operate machinery while tired or under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
- Always disconnect power tools before making adjustments or cleaning them.
- Use push sticks and featherboards when working with power tools to keep your hands away from the blade.
- Never leave tools unattended, especially power tools.
- Be aware of your surroundings and avoid distractions.
- Use a first aid kit for minor injuries.
- Report any accidents or near misses to ensure safety improvements.
Safety Equipment and Their Uses
| Safety Equipment | Uses |
|---|---|
| Safety Glasses | Protect eyes from flying debris, dust, and splinters. |
| Hearing Protection | Reduce noise exposure to prevent hearing damage. |
| Dust Mask | Filter out wood dust and other airborne particles. |
| Work Gloves | Protect hands from cuts, splinters, and burns. |
| First Aid Kit | Provide immediate care for minor injuries. |
Building with Workshop Woodworking Plans
You’ve chosen your plans, gathered your materials, and set up your workshop. Now it’s time to get building! This section will guide you through the process of turning your plans into a finished project, covering everything from preparing your workspace to troubleshooting common problems.
Preparing Your Workspace and Materials
Before you begin building, it’s essential to have a clean and organized workspace. This will help you work more efficiently and safely.
* Clear the area: Remove any clutter or obstacles from your workspace.
* Ensure adequate lighting: Good lighting is crucial for accurate cuts and assembly.
* Have your tools ready: Gather all the tools you’ll need, including measuring tools, saws, clamps, and fasteners.
* Organize your materials: Sort and arrange your lumber, hardware, and other materials.
Common Techniques for Cutting and Assembling Wood
Once your workspace is prepared, you can start cutting and assembling your project.
Cutting Wood
There are several common techniques for cutting wood, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
* Hand saws: Hand saws are versatile and portable, but they can be time-consuming for larger projects.
* Power saws: Power saws, such as circular saws and table saws, are faster and more accurate for straight cuts.
* Jigsaws: Jigsaws are ideal for curved cuts and intricate shapes.
* Router: Routers are used for creating precise edges and decorative details.
Assembling Wood
Once you’ve cut your pieces, you’ll need to assemble them. Here are some common techniques:
* Glue: Wood glue is a strong and durable adhesive that’s suitable for most woodworking projects.
* Screws: Screws provide strong mechanical fastening and are often used in conjunction with glue.
* Nails: Nails are a quick and easy way to join pieces of wood, but they are not as strong as screws.
* Clamps: Clamps are essential for holding pieces of wood together while glue dries.
* Pocket holes: Pocket holes are a technique for joining wood pieces using screws that are inserted at an angle.
Troubleshooting Common Woodworking Problems
Even experienced woodworkers encounter problems. Here are some common issues and solutions:
* Wood splitting: This can occur when driving screws or nails too close to the edge of the wood. To prevent this, use a drill bit that is slightly smaller than the screw or nail diameter to pre-drill a hole.
* Glue squeeze-out: Excess glue can make a messy finish. Use a damp cloth to wipe away excess glue before it dries.
* Wood movement: Wood can expand and contract due to changes in humidity. To minimize movement, use wood that has been properly dried and acclimated to your workshop environment.
* Uneven surfaces: If your project has uneven surfaces, you can use a sanding block or plane to smooth them out.
Finishing and Refinishing
The final step in any woodworking project is finishing, which enhances the wood’s natural beauty and protects it from the elements. Refinishing, on the other hand, is the process of restoring an old or damaged piece of furniture to its former glory.
Types of Wood Finishes
Different wood finishes serve different purposes. Here’s a breakdown of common types:
- Oil-based finishes: These finishes, such as tung oil, linseed oil, and Danish oil, penetrate the wood, enhancing its natural grain and providing a durable protective layer. They offer a warm, natural look and are easy to apply. However, they require multiple coats and can take a long time to dry.
- Varnish: Varnish is a clear, hard-drying finish that protects wood from scratches, moisture, and UV damage. It comes in gloss, semi-gloss, satin, and matte finishes. Varnish provides a durable, protective layer but can be difficult to apply without brush strokes.
- Polyurethane: Polyurethane is a durable, water-based finish that offers excellent protection against water, scratches, and UV damage. It dries quickly and comes in various finishes, including gloss, semi-gloss, satin, and matte. However, polyurethane can be difficult to apply evenly and may require sanding between coats.
- Lacquer: Lacquer is a fast-drying, durable finish that provides a smooth, hard, and protective coating. It is often used on furniture and musical instruments. Lacquer is available in gloss, semi-gloss, satin, and matte finishes. However, it can be difficult to apply without imperfections and requires a well-ventilated area.
- Shellac: Shellac is a natural finish made from the secretions of the lac insect. It is a durable, breathable finish that provides a warm, amber-colored tone. Shellac is often used on furniture and wood floors. It is easy to apply and dries quickly, but it is not as durable as other finishes.
- Wax: Wax is a soft, natural finish that provides a protective layer and enhances the wood’s natural beauty. It is easy to apply and can be used on furniture, floors, and other wood surfaces. Wax is not as durable as other finishes, but it can be easily reapplied.
Applying a Wood Finish
Applying a wood finish can be a rewarding experience, enhancing the beauty of your woodworking project. Follow these steps for a professional-looking finish:
- Prepare the surface: Ensure the wood surface is clean, smooth, and free of dust or debris. Sand the wood with progressively finer grit sandpaper, starting with coarse grit and finishing with fine grit. This removes any imperfections and creates a smooth surface for the finish to adhere to.
- Apply the finish: Choose a finish that complements your project’s style and desired durability. Use a high-quality brush or a clean cloth to apply the finish evenly. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application and drying time.
- Sand between coats: For most finishes, sanding between coats is necessary to create a smooth, even finish. Use fine-grit sandpaper to lightly sand the surface before applying the next coat. This removes any imperfections and creates a smooth, uniform finish.
- Apply multiple coats: Apply multiple coats of finish to achieve the desired level of protection and depth. Allow each coat to dry completely before applying the next.
- Finish with a top coat: A top coat, such as a clear varnish or polyurethane, provides an extra layer of protection and enhances the finish’s durability.
Refinishing Existing Wood Furniture
Refinishing furniture is a great way to give it a new lease on life. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Strip the old finish: Remove the existing finish using a chemical stripper, sanding, or heat gun. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully for safety and effectiveness.
- Sand the surface: Sand the wood surface with progressively finer grit sandpaper to remove any remaining finish, imperfections, and create a smooth surface for the new finish.
- Clean the surface: Thoroughly clean the wood surface to remove any dust or debris from sanding.
- Repair any damage: Fill any cracks, holes, or other damage with wood filler. Allow the filler to dry completely before sanding it smooth.
- Apply a new finish: Apply a new finish to the furniture, following the same steps as for applying a finish to a new piece of wood.
Ultimate Conclusion
With the right workshop woodworking plans and a bit of dedication, you can unlock a world of creative possibilities. From simple projects to ambitious masterpieces, the journey of woodworking is both rewarding and fulfilling. So, gather your tools, choose your plans, and embark on a woodworking adventure that will leave you with a sense of accomplishment and a beautiful piece to showcase your skills.
FAQ Resource
What are the best resources for finding free woodworking plans?
There are many websites and blogs that offer free woodworking plans. Some popular options include Ana White, Woodworking for Mere Mortals, and The Wood Whisperer. These resources often feature a wide variety of plans for different skill levels.
What tools do I need to get started with woodworking?
A basic set of woodworking tools includes a saw, hammer, drill, measuring tape, and screwdrivers. You can also invest in a table saw, router, and sander as your skills progress.
How do I choose the right woodworking plan for my skill level?
Most woodworking plans are categorized by difficulty level, ranging from beginner to advanced. Start with simpler projects and gradually work your way up to more challenging ones as you gain experience.
Workshop woodworking plans are a great way to get started with building your own furniture or other projects. You can find a wide variety of plans online, including woodworking plans that are specifically designed for beginners. Once you have a plan, you can gather your materials and tools and start building! Workshop woodworking plans can help you create anything from simple shelves to complex cabinets.
